Authentication for Connect apps
Ending Connect support
Bitbucket Cloud is gradually ending support for Connect apps.
New Bitbucket apps built with Connect can no longer be registered or installed on workspaces as of Februrary 2, 2026.
Forge is now the Atlassian Cloud's primary platform for extensions. Get started with Forge
On this page you'll find information about authentication methods for Atlassian Connect for Bitbucket.
Getting started
The purpose of this section is to describe how an app can authenticate with Atlassian Connect when making API calls to Atlassian products or exposing endpoints called by an Atlassian product. Atlassian Connect uses a technology called JWT (JSON Web Token) to authenticate apps. Basically, a security context is exchanged when the app is installed, and this context is used to create and validate JWT tokens, embedded in API calls.
The use of JWT tokens guarantees that:
- The Atlassian application can verify it is talking to the app, and vice versa (authenticity).
- None of the query parameters of the HTTP request, nor the path (excluding the context path), nor the HTTP method, were altered in transit (integrity).
Here is how your app can leverage Atlassian Connect's authentication feature:
- You declare that the app uses JWT as the authentication mechanism in the app descriptor.
- You implement an installation callback endpoint, and add a reference to it in the app descriptor.
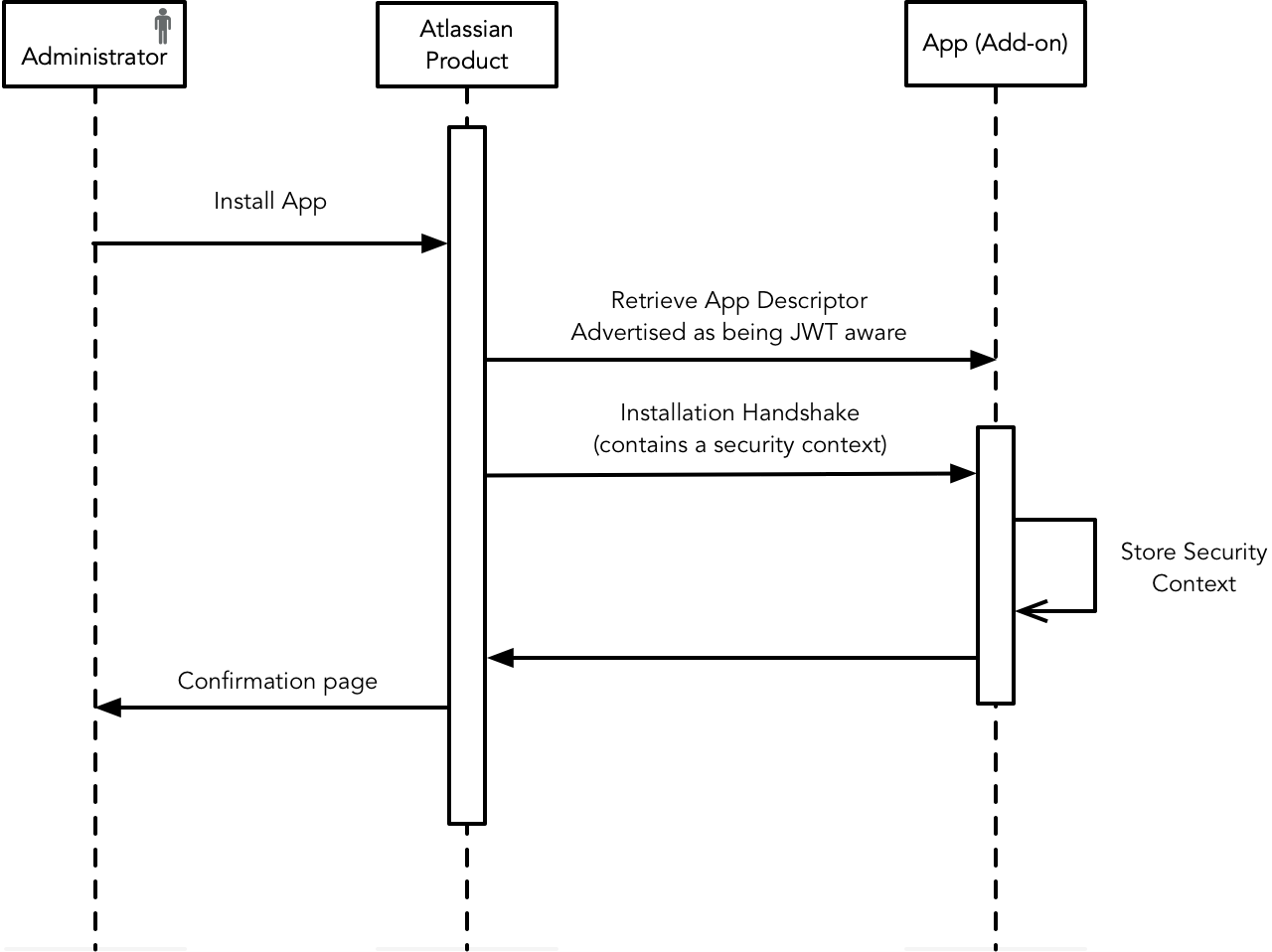
- When an administrator installs the app in an Atlassian cloud instance, Connect initiates an "installation handshake": it invokes the endpoint, passing a security context. You must then store this security context for future use.
- The security contexts contains, among other things, a key identifying the app and a shared secret (used to create and validate JWT tokens). The shared secret can be up to 128 characters in length.
- You then use the security context to validate incoming requests (e.g. Webhooks), and sign outgoing requests (e.g. REST API calls to Jira).
Installation handshake
The installation handshake is a way for the Atlassian application and the app to exchange keys stored on both sides for future API calls.
Signing of the Lifecycle Callbacks
When JWT authentication is used the lifecycle callbacks are signed using a shared secret.
| Use Case | Shared Secret used to Sign |
|---|---|
| First install | None; no JWT token. Because there was no previous shared secret the recipient cannot validate a JWT token. |
| Second and subsequent installs | The shared secret sent in the preceding installed callback. |
| Uninstall, Enable and Disable | The shared secret sent in the preceding installed callback. |
| First install after being uninstalled | The shared secret sent in the preceding installed callback. This allows apps to allow the new installation to access previous tenant data (if any exists).A valid signature demonstrates that the sender is in possession of the shared secret from when the old tenant data was accessed. |
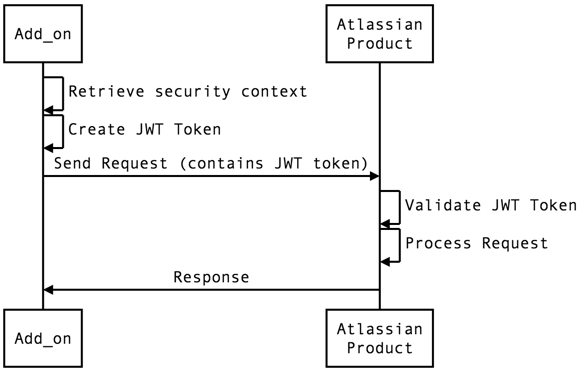
Making a service call
When an app calls an API exposed by an Atlassian product, it must add a valid JWT token to the request, created using the security context provided during the installation handshake.
Exposing a service
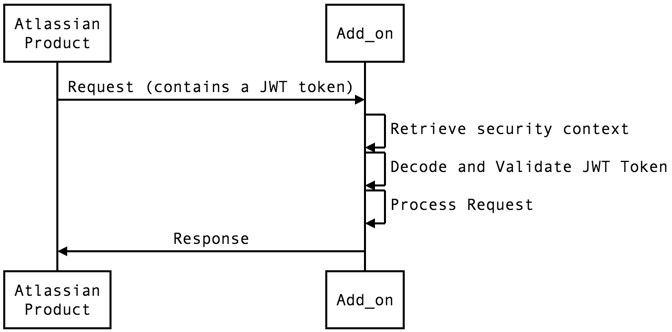
When an Atlassian product calls an API exposed by the app, it is the app's responsibility to validate the JWT token, using the security context provided during the installation handshake.
Authentication how-to
Creating the app descriptor
For an Atlassian Connect app to authenticate securely with the host Atlassian product, it must advertise itself as
being JWT aware, and provide a resource to receive important installation information. This is done by specifying the
elements authentication and lifecycle.
The lifecycle:installed property is a URL which is synchronously called by the Atlassian application when the app
is installed.
For example:
1 2{ "baseUrl": "http://localhost:3000", "key": "atlassian-connect-addon", "authentication": { "type": "jwt" }, "lifecycle": { "installed": "/add-on-installed-callback" } "modules": {} // etc }
Installation data
When the app is installed, the Atlassian application invokes a callback endpoint exposed by the app. The request contains a payload with important tenant information that you will need to store in your app in order to sign and verify future requests.
For details on the contents of the payload, please see the lifecycle attribute documentation.
Understanding JWT
Knowledge of JWT is a prerequisite. Check out the Understanding JWT for apps page if you are unfamiliar with JWT.
Making a service call
The JWT protocol describes the format and verification of individual JWT tokens. Atlassian Connect for Bitbucket only supports authorization headers as the method of transport. When communicating server-to-server with the Bitbucket, your app must include a JWT token when accessing protected resources. This covers most of the REST APIs. Construct a token that identifies your app, identifies the query, specifies the token's expiry time and allows the receiver to verify that this token was genuinely constructed by your app.
Example:
1 2POST https://api.bitbucket.org/2.0/repositories/teamsinspace/documentation-tests/pullrequests "Authorization" header value: "JWT <insert jwt-token here>"
For more details on how to create a jwt token, see Creating a JWT Token.
Exposing a service
All incoming requests (requests coming from an Atlassian product) should check for the presence of the jwt query string parameter, which needs to be decoded and verified. In particular, the verification should:
- Extract the JWT token from the request's
jwtquery parameter or the authorization header.
- Decode the JWT token, without verification. This gives you a header JSON object, a claims JSON object, and a signature.
- Extract the issuer ('iss') claim from the decoded, unverified claims object. This is the
clientKeyfor the tenant - an identifier for the Atlassian application making the call, which should have been stored by the app as part of the installation handshake. - Look up the
sharedSecretfor theclientKey, as stored by the app during the installation handshake - Verify the signature with the
sharedSecretand the algorithm specified in the header'salgfield. - Verify the query has not been tampered by Creating a Query Hash and comparing it against the
qshclaim on the verified token. - The JWT specification lists some standard claims that, if present, you should verify. Issuers include these to help you ensure that tokens you receive are used according to the intentions of the issuer and with the best possible results.
These steps must be executed before processing the request, and the request must be rejected if any of these steps fail.
For more details on how to decode and validate a JWT token, see Decoding and Verifying a JWT Token, which also provides a comprehensive list of claims supported by Atlassian products that you need to validate.
Rate this page: