Build a Teamwork Graph connector
Teamwork Graph connectors are available through Forge's Early Access Program (EAP).
EAPs are offered to selected users for testing and feedback purposes. We are currently working with a select group of EAP participants to get their apps production-ready and available for publishing on Marketplace.
If you are interested in joining this EAP, you can express interest through this form.
This tutorial demonstrates how to add data to Atlassian's Teamwork Graph using the Forge Teamwork Graph connector module and Connector SDK APIs.
You’ll build a Jira app that can fetch data from a third-party system, store the objects in Teamwork Graph, and then fetch an object using its ID.
In this tutorial, we’ll use a web trigger to invoke our methods. For related details, see Web triggers and webtrigger Operation. Note that this tutorial only demonstrates the backend of the app. It doesn’t include any frontend components, such as UI Kit.
Example app
To view the app code for this tutorial, check out the example app.
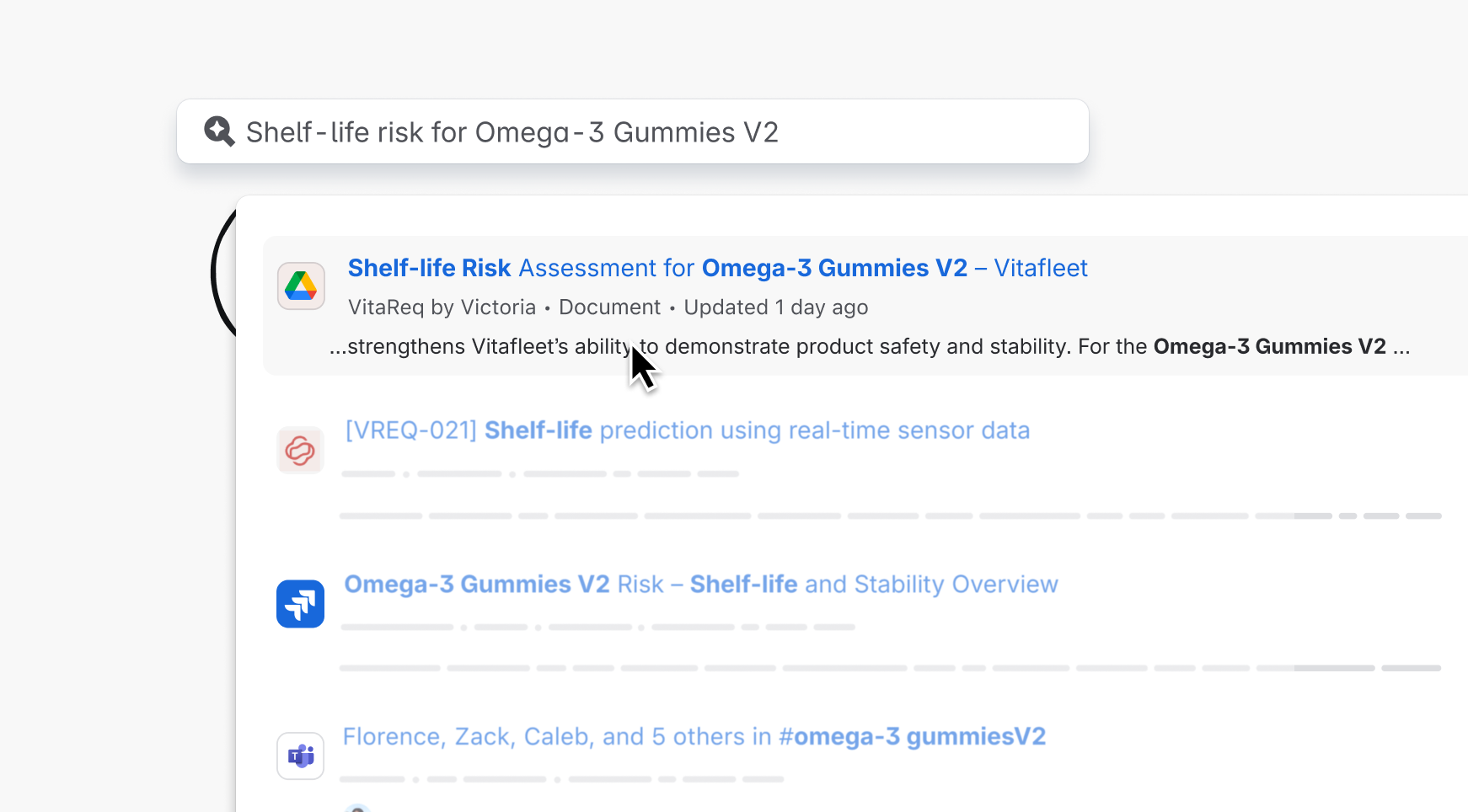
Connect Google Drive to Teamwork Graph
A Teamwork Graph connector to add Google Drive data to Atlassian's Teamwork Graph.
Before you begin
This tutorial assumes you're already familiar with developing on Forge. If this is your first time using Forge, see Getting started for step-by-step instructions on setting up Forge.
To complete this tutorial, you need the following:
- The latest version of Forge CLI. To update your CLI version, run
npm install -g @forge/cli@lateston the command line. - An Atlassian site with Jira where you can install your app.
Currently, apps that use Teamwork Graph modules will need to be installed into Jira. This means that in order to test your Teamwork Graph app, you will need a Jira site. If you don't have one of these already, set one up at http://go.atlassian.com/cloud-dev.
Step 1: Create your app
We will start by creating a blank Forge app. You can do this using the terminal:
- Navigate to the directory where you want to create the app.
- Create your app by running:
1 2
forge create - Enter a name for the app. For example, sample-teamwork-graph-connector.
- Select the Show All category.
- Select Show All for the product.
- Select the blank template.
- Your app has been created in a directory with the same name as your app; for example sample-teamwork-graph-connector. Open the app directory to see the files associated with your app.
Step 2: Configure the app manifest
Make the following changes in manifest.yml file of the app.
-
Add
permissionsto the app as shown below. Replace thebackendurl with the endpoint you want to fetch data from. To learn more, see Permissions.1 2
permissions: scopes: - write:object:jira - read:object:jira - delete:object:jira external: fetch: backend: - "https://www.googleapis.com" -
Add the
graph:connectormodule undermodules. For more information on this module, see Teamwork Graph connector.1 2
modules: graph:connector: - key: google-drive-connector name: Google Drive icons: light: https://static.example-hello-world.com/favicon-light.ico dark: https://static.example-hello-world.com/favicon-dark.ico objectTypes: - atlassian:document datasource: formConfiguration: form: - key: connectionDetails type: header title: Connection Details description: Please provide your Google Drive API Key and Folder ID properties: - key: apiKey label: Api Key type: string isRequired: true - key: folderId label: Google Drive Folder ID type: string isRequired: true validateConnection: function: validateConnectionFn instructions: - 1. Enable Google Drive API on Google Cloud - 2. Add an API Key and Google Drive Folder ID onConnectionChange: function: onConnectionChangeFn
Here, you have defined the Teamwork Graph connector, including:
- The object types it supports. In this example,
atlassian:document. - The configuration details that will appear in Atlassian Administration, allowing an admin to set up the connector.
The datasource property in this module also enables:
-
Connection validation (
validateConnectionFn): Ensures that the details entered by the admin, such as API keys or folder IDs, are correct before the connection is saved.1 2
import { fetch } from '@forge/api'; // Connection management types for graph connector export interface ConnectionRequest { name: string; configProperties: Record<string, any>; } export interface ConnectionResponse { success: boolean; message?: string; } export interface ValidateConnectionRequest extends ConnectionRequest {} export interface ValidateConnectionResponse extends ConnectionResponse {} export const validateConnection = async (request: ValidateConnectionRequest): Promise<ValidateConnectionResponse> => { try { console.log('Validating connection:', request.name); const apiKey = request.configProperties.apiKey; const folderId = request.configProperties.folderId; if (!apiKey || !folderId) { return { success: false, message: 'Either API key or folderId is missing' }; } // Test the API key by making a simple request to Google Drive API const testUrl = `https://www.googleapis.com/drive/v3/files?q='${folderId}'%20in%20parents&key=${apiKey}`; const response = await fetch(testUrl, { method: 'GET', headers: { 'Accept': 'application/json' } }); if (!response.ok) { const errorText = await response.text(); console.error('API validation failed:', response.status, errorText); return { success: false, message: `API key validation failed: ${response.status} ${response.statusText}` }; } const data = await response.json() as GoogleDriveApiResponse; console.log('API validation successful for folderId: ', folderId, ' with data size: ', data.files.length); return { success: true, message: 'Connection validated successfully' }; } catch (error) { console.error('Error validating connection:', error); return { success: false, message: `Connection validation error: ${error instanceof Error ? error.message : 'Unknown error'}` }; } }; -
Connection change handling (
onConnectionChangeFn): Automatically responds to changes made by the admin, such as updating or deleting a connection.1 2
import { kvs } from '@forge/kvs'; export interface ConnectorConfig { connectorName?: string; connectionId?: string; apiKey?: string; folderId?: string; } export interface OnConnectionChangeRequest extends ConnectionRequest { action: 'CREATED' | 'UPDATED' | 'DELETED'; connectionId: string; } export interface OnConnectionChangeResponse extends ConnectionResponse {} export const onConnectionChange = async (request: OnConnectionChangeRequest): Promise<OnConnectionChangeResponse> => { try { console.log('Connection change event:', request); const connectorConfig: ConnectorConfig = { connectorName: request.configProperties.connectorName, connectionId: request.connectionId, apiKey: request.configProperties.apiKey, folderId: request.configProperties.folderId }; console.log('Connector config:', JSON.stringify(connectorConfig)); switch (request.action) { case 'CREATED': console.log('New connection created:', request.name); await kvs.setSecret(request.name, connectorConfig); // Here you could initialize any resources needed for the new connection // For example, create initial data sync jobs, set up webhooks, etc. break; case 'UPDATED': console.log('Connection updated:', request.name); await kvs.setSecret(request.name, connectorConfig); // Here you could handle configuration changes // For example, update sync settings, refresh tokens, etc. break; case 'DELETED': console.log('Connection deleted:', request.name); await kvs.deleteSecret(request.name); // Here you could clean up resources associated with the connection // For example, cancel sync jobs, remove webhooks, clean up cached data, etc. break; default: console.warn('Unknown change type:', request.action); } return { success: true, message: `Connection ${request.action} handled successfully` }; } catch (error) { console.error('Error handling connection change:', error); return { success: false, message: `Connection change error: ${error instanceof Error ? error.message : 'Unknown error'}` }; } };
Step 3: Deploy and install your app
Currently, apps that use Teamwork Graph modules will need to be installed into a Jira site.
You must run the forge deploy command before running the forge install command because an
installation links your deployed app to an Atlassian site.
-
Navigate to the app's top-level directory and deploy your app by running:
1 2
forge deploy -
Install your app by running:
1 2
forge install -
Select
Jirausing the arrow keys and press the enter key. -
Enter the URL for your development site. For example, example.atlassian.net. View a list of your active sites at Atlassian administration.
Once the successful installation message appears, your app is installed and ready to use on the
specified site. You can always delete your app from the site by running the forge uninstall command.
Step 4: Connect your app through Atlassian Administration
Once the app is installed on the site, an organization admin can visit Connected apps in Atlassian Administration page to configure the connector.
-
Go to Atlassian Administration.
-
Select Apps in the left-hand navigation, then select the site where the app is installed, and then select Connected apps. All installed apps, including the one we added with the Forge Teamwork Graph connector, will appear on this page.
-
Once you find your app on this page, select View app details.
-
Navigate to the Connections tab.
-
Under Teamwork Graph connectors, select Connect for your Teamwork Graph connector.
-
Fill out the fields in the configuration screen to set up the connector. In this example, that includes the connector nickname, your Google Drive API key, and Folder ID. See below for how to get your Google Drive API key.
-
Once all details have been added, click Connect to initiate the connection with the external service.
Getting a Google Drive API key
To test this app, you’ll need a Google Drive API key. To get your Google Drive API key:
-
Open the Google Cloud Console: https://console.cloud.google.com/
-
Select or create a project: Choose an existing project, or click New Project to create one.
-
Enable the Google Drive API:
- Navigate to APIs & Services > Library
- Search for “Google Drive API”
- Click Enable
-
Create an API key:
- Go to APIs & Services > Credentials
- Click Create credentials > API key
- Copy the generated API key
-
(Recommended) Restrict your API key:
- On the API key page, click Edit API key
- Application restrictions: For server-to-server calls (Forge runtime), set to None
- API restrictions: Click Restrict key, then select Google Drive API
- Click Save
API keys can only access public or shared resources. If your Drive folder or files are private, either:
- Share the folder as “Anyone with the link” (suitable for demos), or
- Use OAuth 2.0 or a Service Account for private access (not covered in this tutorial)
Step 5: Add a web trigger for fetching data
We’ll now add a function for fetching data.
When using web triggers, always consider the security and authentication implications. For simplicity, this tutorial does not include an authentication mechanism.
-
In the
src/directory, add a new file namedobjects.tswith the following contents:Types
1 2
// Type definitions for Google Drive API response interface GoogleDriveFile { id: string; name?: string; mimeType?: string; createdAt?: string; lastUpdatedAt?: string; } interface GoogleDriveApiResponse { files: GoogleDriveFile[]; } // Connection config object interface ConnectorConfig { connectorName?: string; connectionId?: string; apiKey?: string; folderId?: string; } // Request interfaces - Compatible with Forge WebtriggerRequest interface ApiRequest { queryParameters?: { [key: string]: any; externalId?: string; objectType?: string; objectIds?: string; connectorName?: string; }; body?: string; headers?: Record<string, string>; method?: string; path?: string; } interface ApiResponse<T = any> { body: T; statusCode: number; }1 2
import { graph } from '@forge/teamwork-graph'; import { FetchDataResponse } from '@forge/teamwork-graph/out/types'; export async function fetchData(request: ApiRequest, connectorConfig: ConnectorConfig): Promise<ObjectApiResponse<GoogleDriveApiResponse | string>> { console.log('fetchData called with request:', request); try { // Get the connector name from the request if (!connectorConfig.connectorName) { return { body: 'Missing required parameter: connectorName. Please provide a connectorName to fetch the data.', statusCode: 400 }; } const apiKey = connectorConfig.apiKey; const folderId = connectorConfig.folderId; console.log('Using Folder ID:', folderId); const requestConfig = { url: `https://www.googleapis.com/drive/v3/files?q='${folderId}'%20in%20parents&key=${apiKey}`, method: 'GET' as const, headers: { 'Accept': 'application/json' } }; const response = await fetch(requestConfig.url, { headers: requestConfig.headers, method: requestConfig.method }); console.log("fetch response: ", response); if (!response.ok) { throw new Error('Failed to fetch data from Google Drive API: ' + response.statusText); } const data = await response.json(); console.log("data: ", data); const googleDriveApiResponse: GoogleDriveApiResponse = data; console.log('Parsed GoogleDriveApiResponse:', googleDriveApiResponse); // Validate the response structure if (!googleDriveApiResponse.files) { throw new Error('Invalid response structure: missing files array'); } return { body: googleDriveApiResponse, statusCode: 200 }; } catch (error) { console.error('Error in fetchData:', error); return { body: 'Error fetching data: ' + (error as Error).message, statusCode: 500 }; } }The
objects.tsfile contains a function calledfetchDatathat uses the connection object stored in KVS to retrieve the Google API Key andfolderId, then calls Google Drive to fetch files from the specified folder.
-
Update the
index.tsfile with the following:Types
1 2
interface WebtriggerRequest { body?: string; headers: Record<string, string>; method: string; path: string; queryParameters: Record<string, string>; } interface WebtriggerResponse<T = any> { statusCode: number; body: T; headers?: Record<string, string>; }1 2
import { kvs } from '@forge/kvs'; import { fetchData } from './objects'; async function extractConnectionConfig(request: WebtriggerRequest): Promise<ConnectorConfig> { const connectorName = request.queryParameters?.connectorName?.toString().trim(); if (connectorName) { return await kvs.getSecret(connectorName as string) as ConnectorConfig; } return {} as ConnectorConfig; } export const googleIngestion = async ( request: WebtriggerRequest): Promise<WebtriggerResponse> => { // Debug: Log the entire queryParameters object console.log('TS: Full queryParameters:', request.queryParameters); try { // Try multiple possible parameter names and clean the value let action = request.queryParameters?.func || request.queryParameters?.action || request.queryParameters?.function; // Clean the action value (trim whitespace and normalize case) action = action?.toString().trim(); console.log('Extracted action:', action); console.log('Action type:', typeof action); console.log('Action length:', action?.length); let connectorConfig: ConnectorConfig = await extractConnectionConfig(request); console.log('Connector name:', connectorConfig.connectorName); console.log('Connection ID:', connectorConfig.connectionId); switch (action) { case 'fetchData': const data = await fetchData(request, connectorConfig); console.log('FetchData response:', data); return { statusCode: 200, body: 'Data fetched successfully. Files count: ' + (data.body as any).files.length }; default: console.log('Going to default case, action was:', JSON.stringify(action)); return { statusCode: 400, body: `Invalid action parameter. Received: \"${action}\". Expected: \"fetchData\"` }; } } catch (error) { console.error('Error in exampleWebtrigger:', error); return { statusCode: 500, body: `Internal server error: ${error instanceof Error ? error.message : 'Unknown error'}` }; } }; -
Modify the
manifest.ymlto add this new endpoint to themodulessection and delete the existing function with keymy-function.1 2
webtrigger: - key: google-ingestion-webtrigger function: google-ingestion function: - key: google-ingestion handler: index.googleIngestion -
Re-deploy and verify your changes in the app by running:
1 2
forge deploy
Invoke your app
To use the web trigger in this tutorial, you’ll need a tool for making HTTP requests, such as curl.
- Find the URL by using
forge webtrigger. - Choose the relevant site.
- The web trigger will have the name
google-ingestion-webtrigger. - Send a
GETrequest to this URL.
Example curl command:
1 2curl 'your-webtrigger-url?func=..'
Step 6: Add an API for setting objects
After using the googleIngestion web trigger to fetch data, we can now implement the ability to
save objects.
-
Add these methods in the
objects.tsfile.1 2
/** * Processes the setObjects API request and handles the response */ async function processsetObjectsRequest(documents: DocumentObject[], connectionId: string): Promise<ApiResponse<string>> { const setObjectsResponse: BulkObjectResponse = await graph.setObjects({ objects: documents as any, connectionId: connectionId }); console.log("setObjectsResponse: ", setObjectsResponse); if (setObjectsResponse.success) { return { body: 'objects set successfully', statusCode: 200 }; } else { return { body: 'Error setting objects: ' + setObjectsResponse.error, statusCode: 500 }; } } /** * Transforms Google Drive file data into Atlassian document objects */ function transformData(data: GoogleDriveApiResponse, folderId: string): DocumentObject[] { const files = data.files; console.log("files: ", files); return files.map((item: GoogleDriveFile, idx: number): DocumentObject => ({ schemaVersion: '1.0', id: item.id || \`doc-\${idx}\`, updateSequenceNumber: 1, displayName: item.name || 'Untitled Document', url: 'https://drive.google.com/file/d/' + item.id + '/view?usp=drive_link', createdAt: item.createdAt || new Date().toISOString(), permissions: [{ accessControls: [ { principals: [{ type: 'EVERYONE' }] } ] }], parentKey: { type: 'atlassian:document', value: { entityId: folderId } }, associations: { set: [ { associationType: 'issueIdOrKeys', values: ['Test'], } ] }, lastUpdatedAt: item.lastUpdatedAt || new Date().toISOString(), 'atlassian:document': { type: { category: 'image', // TODO: get category from mimeType mimeType: item.mimeType || 'Unknown', }, content: { mimeType: item.mimeType || 'Unknown', text: 'Sample document content', } } })); } export async function setObjects(request: ApiRequest, connectorConfig: ConnectorConfig): Promise<ApiResponse<string>> { console.log('setObjects called with request:', request); try { const response = await fetchData(request, connectorConfig); if (response.statusCode !== 200 || typeof response.body === 'string') { return { body: 'Error fetching data: ' + response.body, statusCode: response.statusCode }; } const data = response.body as GoogleDriveApiResponse; console.log("data: ", data); const folderId = connectorConfig.folderId; let documents: DocumentObject[] = transformData(data, folderId); console.log("transformedData: ", documents); const setObjectsResponse = await processsetObjectsRequest(documents, connectorConfig?.connectionId as string); if (setObjectsResponse.statusCode === 500) { return setObjectsResponse; } documents = []; documents.push(createFolderDocument(folderId)); return await processsetObjectsRequest(documents, connectorConfig?.connectionId as string); } catch (error) { console.error('Error setting objects:', error); return { body: 'Error setting objects: ' + (error as Error).message, statusCode: 500 }; } } function createFolderDocument(folderId: any): DocumentObject { // Create a folder document object from folderId and return return { schemaVersion: '1.0', id: folderId, updateSequenceNumber: 1, displayName: 'Google Drive Folder', url: \`https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/\${folderId}\`, createdAt: new Date().toISOString(), permissions: [{ accessControls: [ { principals: [{ type: 'EVERYONE' }] } ] }], lastUpdatedAt: new Date().toISOString(), 'atlassian:document': { type: { category: 'folder', }, content: { mimeType: 'application/vnd.google-apps.folder', text: 'Google Drive Folder', } } }; }setObjectsfirst fetchesconnectorConfigfrom the key-value store using theconnectorNamefrom the request. After retrieving theconnectorConfig, it uses the API Key andfolderIdto get data from the Google Drive API. It then transforms the data into a supported format - in this case,atlassian:document. Finally, all fetched files and folders converted into documents are provided to Atlassian’s Teamwork Graph. -
Update the
index.jsfile to add case forsetObjects.1 2
case 'setObjects': return await setObjects(request, connectorConfig);Example
curlcommand to use thesetObjectsfunction:1 2
curl '$URL?func=setObjects&connectorName=<connector-name>'
Step 7: Add an API for fetching objects
-
Add this method in the
objects.tsfile:Types
1 2
interface ObjectResponse { message: string; externalId: string; objectType: string; data: any; }1 2
export async function getObject(request: ApiRequest, connectorConfig: ConnectorConfig): Promise<ApiResponse<ObjectResponse | string>> { console.log('getObject called with request:', request); try { // Extract externalId and objectType from request parameters let externalId: string | null = null; let objectType: string = 'atlassian:document'; // Default object type // Try to get parameters from query parameters first if (request.queryParameters?.externalId) { const rawExternalId = request.queryParameters.externalId; externalId = String(rawExternalId).trim(); } if (request.queryParameters?.objectType) { const rawobjectType = request.queryParameters.objectType; objectType = String(rawobjectType).trim(); } console.log('External ID:', externalId); console.log('Object type:', objectType); // Validate required parameters if (!externalId) { return { body: 'Missing required parameter: externalId. Please provide an externalId to retrieve the object.', statusCode: 400 }; } const data = await graph.getObjectByExternalId({ externalId: externalId, objectType: objectType, connectionId: connectorConfig?.connectionId }); console.log("getObject response: ", data); if (data.success) { return { body: JSON.stringify(data.object), statusCode: 200 }; } else { return { body: 'Error getting object: ' + data.error, statusCode: 500 }; } } catch (error) { console.error('Error in getObject:', error); return { body: 'Error getting object: ' + (error as Error).message, statusCode: 500 }; } }Given the provided
externalId, the function retrieves the corresponding object. -
Update
index.tswith this new method case:Types
1 2
interface WebtriggerRequest { body?: string; headers: Record<string, string>; method: string; path: string; queryParameters: Record<string, string>; } interface WebtriggerResponse<T = any> { statusCode: number; body: T; headers?: Record<string, string>; }1 2
import { kvs } from '@forge/kvs'; import { fetchData, getObject, setObjects } from './objects'; export const googleIngestion = async ( request: WebtriggerRequest): Promise<WebtriggerResponse> => { // Debug: Log the entire queryParameters object console.log('TS: Full queryParameters:', request.queryParameters); try { // Try multiple possible parameter names and clean the value let action = request.queryParameters?.func || request.queryParameters?.action || request.queryParameters?.function; // Clean the action value (trim whitespace and normalize case) action = action?.toString().trim(); console.log('Extracted action:', action); console.log('Action type:', typeof action); console.log('Action length:', action?.length); let connectorConfig: ConnectorConfig = await extractConnectionConfig(request); console.log('Connector name:', connectorConfig.connectorName); console.log('Connection ID:', connectorConfig.connectionId); switch (action) { case 'fetchData': const data = await fetchData(request, connectorConfig); console.log('FetchData response:', data); return { statusCode: 200, body: 'Data fetched successfully. Files count: ' + (data.body as any).files.length }; case 'setObjects': return await setObjects(request, connectorConfig); case 'getObject': return await getObject(request, connectorConfig); default: console.log('Going to default case, action was:', JSON.stringify(action)); return { statusCode: 400, body: `Invalid action parameter. Received: \"${action}\". Expected: \"fetchData\", \"setObjects\", \"getObject\"` }; } } catch (error) { console.error('Error in exampleWebtrigger:', error); return { statusCode: 500, body: `Internal server error: ${error instanceof Error ? error.message : 'Unknown error'}` }; } }; async function extractConnectionConfig(request: WebtriggerRequest): Promise<ConnectorConfig> { const connectorName = request.queryParameters?.connectorName?.toString().trim(); if (connectorName) { return await kvs.getSecret(connectorName as string) as ConnectorConfig; } return {} as ConnectorConfig; }An example
curlcommand to use thegetObjectfunction:1 2
curl '$URL?func=getObject&externalId=<someID>&connectorName=<connector-name>'
Troubleshooting
Use forge tunnel for debugging any issue while developing the app. This command displays your
app’s logs in your terminal.
Rate this page: