Relationships
Relationships are the connections between objects in Teamwork Graph that describe how those objects are related. They are fundamental to how Teamwork Graph connects, organizes, and enables insights across Atlassian experiences.
For example, if a Jira work item is linked to a Confluence page, Teamwork Graph stores a relationship between those two objects. This allows features like Rovo, analytics dashboards, automation workflows, or the custom app you are building to "connect the dots" across work.
Key characteristics of relationships include:
-
Every relationship has a type: For example,
UserCreatedIssue,ParentIssueHasChildIssue, orIssueAssociatedPR. -
Relationships are directional: One object is the "from" (starting point) and the other is the "to" (endpoint). For example, in "issue A is-parent-of issue B," the relationship goes from issue A to issue B.
-
They form a semantic network: Relationships form a web of connections that can be queried to answer questions, power analytics, and drive automation.
How relationships are used
Relationships serve different purposes depending on how you interact with Teamwork Graph:
For Teamwork Graph API
If you're querying Teamwork Graph data, relationships allow you to traverse connections between objects. You can:
- Find all work items assigned to a specific user
- Discover which pull requests are associated with a work item
- Navigate from a project to its related goals
- Explore the network of connections across Atlassian data
See the API reference for details on querying relationships.
For Teamwork Graph connectors
If you're building a connector to add data to Teamwork Graph, you'll create relationships between objects using attributes like parentKey, containerKey, createdBy, owners, or associations. These relationships enable Atlassian experiences like Rovo, analytics, and Smart Links to connect your data with other data in the graph.
See the Connector reference for details on creating relationships.
Types of relationships
In Teamwork Graph, there are four types of relationships: canonical, activity, logical, and inferred.
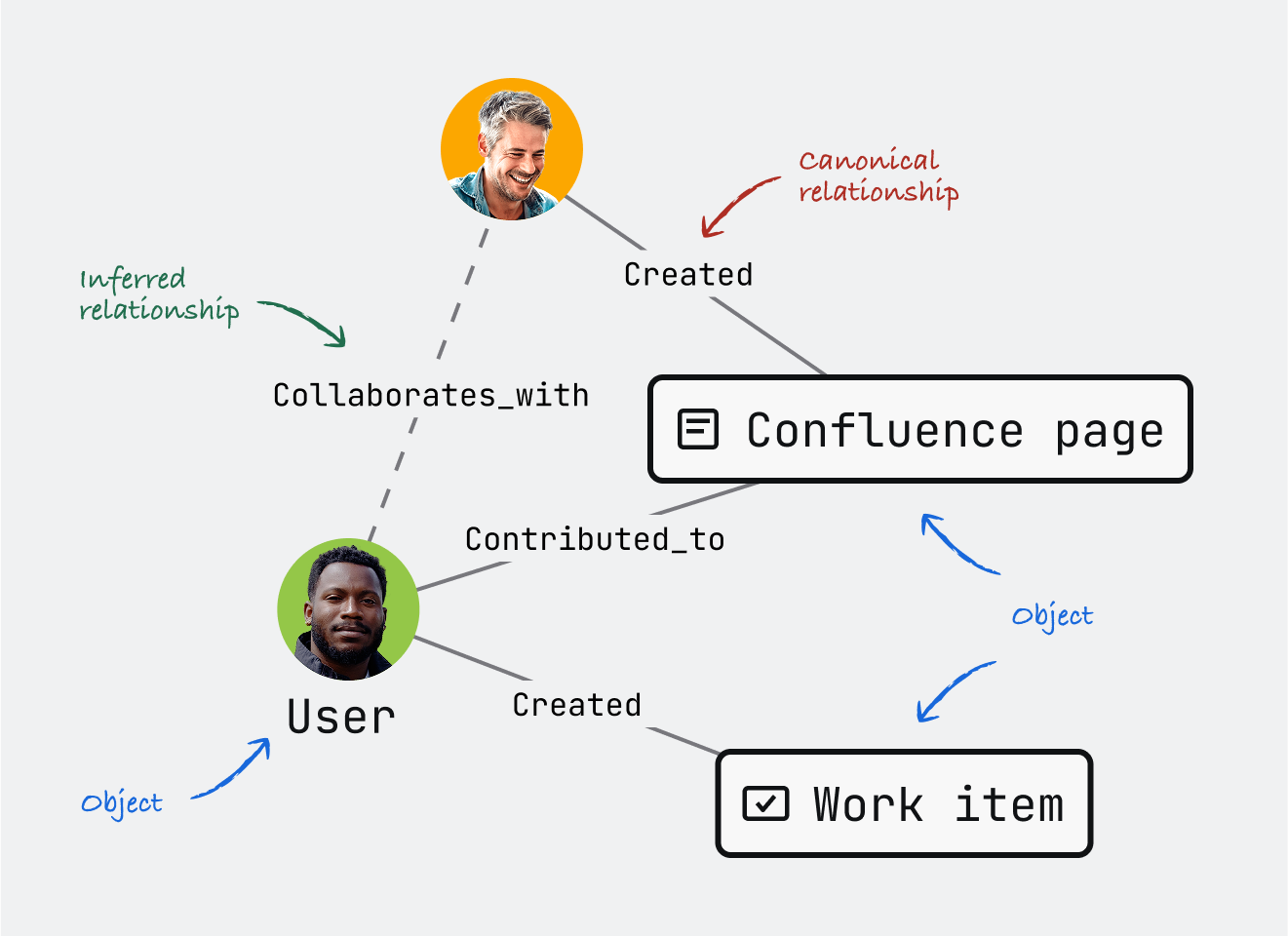
Canonical relationships
Canonical relationships are direct, structural connections between objects in the graph. These define ownership, containment, and logical associations between objects. For example:
- A work item belongs to a project
- A document has a parent document
- A pull request is in a repository
- A commit is associated with a work item
When building connectors, you create canonical relationships using attributes like parentKey, containerKey, or associations. These are the foundational, "source of truth" connections in the graph.
Activity relationships
Activity relationships capture user actions and interactions with objects. These relationships record behavioral data about who did what to which objects. For example:
- A user created a work item
- A user updated a Confluence page
- A user assigned an issue
- A user viewed a project
Activity relationships are automatically generated by Atlassian systems when users interact with objects. They're valuable for understanding collaboration patterns, work history, and user engagement.
Logical relationships
Logical relationships are high-level relationships that encompass multiple underlying relationship types, providing a unified view across different object types. These relationships simplify querying by allowing you to access related objects through a single relationship type, regardless of the specific underlying relationship or object type. For example:
AtlassianUserCreatedDocumentsprovides a unified view of all documents a user has created, whether they're Confluence pages, external documents, or other document typesAtlassianUserAssignedWorkItemsprovides a unified view of all work items assigned to a user, whether they're Jira work items or external work items
Logical relationships are particularly useful when querying the Teamwork Graph API, as they group related object types together, allowing you to query them as a single relationship rather than multiple separate relationships.
Inferred relationships
Inferred relationships are connections that are not directly recorded by explicit actions or events, but are derived by Teamwork Graph itself. These are calculated by analyzing patterns, metadata, or using machine learning models on existing data. For example:
- Inferring "top collaborators" for a user based on their interaction history
- Suggesting relevant work items based on behavioral patterns
Inferred relationships help surface implicit connections and recommendations that might not be obvious from canonical or activity relationships alone.
API relationship types
When you query the Teamwork Graph API, you can access the relationships that connect objects. These include relationships between Jira work items, users, Atlassian projects, and more.
To explore the full list of relationship types available for querying with the Teamwork Graph API:
API relationship types
Explore the relationship types you can query with the Teamwork Graph API.
Connector relationships
When you build a connector and add data to Teamwork Graph, you create relationships between your objects and other data in the graph. These relationships enable Atlassian experiences like Rovo, analytics, and Smart Links to connect your data with other data in the graph.
To learn how to create relationships when building connectors:
Create relationships when building Teamwork Graph connectors
Learn how to create relationships between objects when building Teamwork Graph connectors.
Rate this page: