What is Teamwork Graph?
Teamwork Graph is Atlassian's unified data layer that connects teamwork data from across Atlassian apps, like Jira and Confluence, as well as external tools. It enables organizations to centralize their data, break down silos, and streamline workflows by providing a common data model for work items, documents, messages, users, groups, projects, and more.
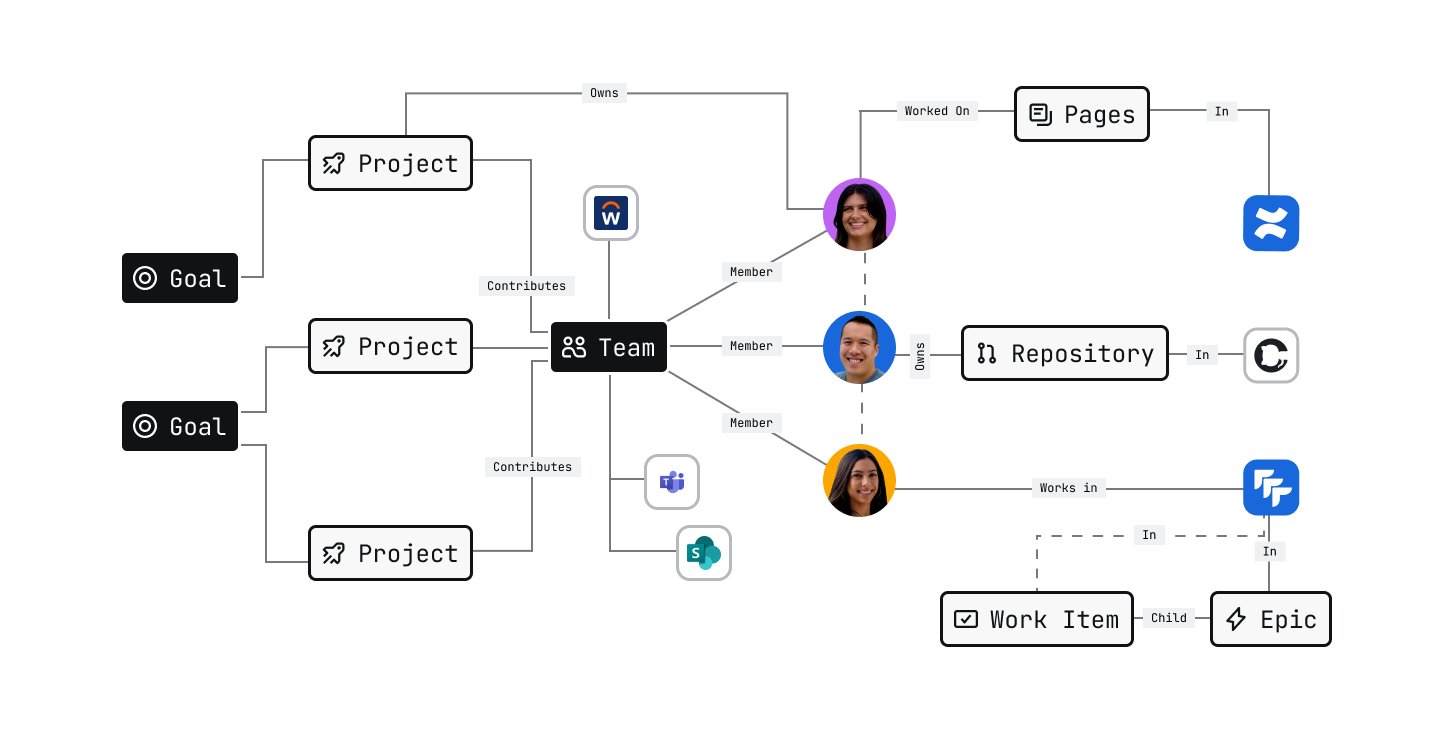
How does Teamwork Graph work?
Unified data model
At its core, Teamwork Graph is a common data model that represents the building blocks of teamwork. Each item—whether it's a Jira work item, Confluence page, Google Drive file, Slack message, or GitHub pull request—is represented in Teamwork Graph as an object.
Every object belongs to a specific object type, which defines its category and the set of properties it has. For example, a work item from Jira, Asana, or GitHub can all be represented using the same object type, even though they come from different systems. This standardization is what makes Teamwork Graph powerful: it allows data from both Atlassian apps and external tools to be integrated, queried, and related in a consistent way.
The unified data model means that regardless of where data originates—whether it's from Jira, Confluence, Google Drive, Slack, or any other connected tool—it can be understood, searched, and connected in the same way. This breaks down the silos that typically exist between different tools and systems.
Teamwork Graph connectors
Teamwork Graph connectors are the mechanism that brings external data into the graph. They enable data from any source—third-party SaaS tools, internal systems, or custom applications—to become part of the unified Teamwork Graph.
Atlassian provides 100 out-of-the-box Teamwork Graph connectors that allow customers to connect popular tools like Google Drive, Slack, GitHub, and many others to Teamwork Graph. These connectors automatically extract data from source systems, map it to Teamwork Graph's object types, and push it into the graph along with relationships and permissions.
The power of connectors is that they transform disparate data sources into a unified graph. A document from Google Drive, a message from Slack, and a work item from Jira can all exist in the same graph, be searched together, and be connected through relationships. This creates a comprehensive view of how work actually happens across an organization, not just within individual tools.
Once data is in Teamwork Graph through connectors, it becomes available across Atlassian experiences like Rovo Search, Chat, Agents, and Atlassian Analytics, making external data as accessible and actionable as native Atlassian data.
Relationships and context
Teamwork Graph doesn't just store individual objects—it maps relationships between them. These relationships are what transform a collection of data points into a meaningful graph that represents how work, people, and information are actually connected.
For example, Teamwork Graph can link a Confluence page to a Jira work item, connect a Slack message to a project, or show that multiple users collaborated on a document. These relationships create context that enables powerful capabilities:
- Unified search can find related content across all tools, not just individual results
- Personalized recommendations can suggest relevant work, documents, or collaborators based on the graph of connections
- Cross-tool automation can understand dependencies and relationships to trigger appropriate actions
- Analytics can reveal patterns and insights that would be invisible when looking at tools in isolation
The relationships in Teamwork Graph create a rich, contextual understanding of how work flows through an organization, making it possible to build experiences that are truly aware of the connections between people, work, and information.
What value does Teamwork Graph provide?
By centralizing data from across tools and mapping the relationships between objects, Teamwork Graph enables organizations to:
- Break down silos: See how work connects across different tools and teams
- Improve productivity: Find information faster and reduce context switching between applications
- Enable smarter insights: Understand patterns and relationships that span multiple tools
- Streamline workflows: Automate processes that involve multiple systems
- Scale integrations: Easily add new tools and data sources as needs evolve
While Teamwork Graph operates behind the scenes as part of the platform, users experience its value through features like unified search, intelligent recommendations, cross-tool analytics, and seamless workflows that span multiple applications.
Rate this page: