Java integration libraries
This page provides sample code for creating a Crowd Client using the supplied Java integration libraries.
We recommend that you use the REST API for long-term compatibility. If you have a Java application, you can use the Java client libraries shipped with Crowd, but please be aware that they may change between releases. You may need to re-compile your source and possibly change a package name.
The CrowdClient is useful for common create, query, update and delete operations for principals, groups and roles. To accomplish this, the CrowdClient makes use of the REST API of the Crowd server. The class reads in the crowd.properties configuration file from your application's class path, setting client specific details such as the Crowd server URL and SSO integration details. When the client is loaded into memory, it will then authenticate the the client application with the Crowd server for future REST requests.
A full list of the available methods for the CrowdClient is available here:
com.atlassian.crowd.integration.http.CrowdHttpAuthenticator
The CrowdHttpAuthenticator simplifies the authentication of HTTP based clients. When an authentication or invalidation is performed, the CrowdHttpAuthenticator manages the setting and resetting of integration variables for the principal's HTTP session. If the application has little need beyond authentication and validation, the CrowdHttpAuthenticator is a simple and very straightforward integration piece. Shown below is a code example of authenticating and logging off a principal:
Example 1:
1 2RestCrowdHttpAuthenticationFactory.getAuthenticator().authenticate(request, response, username, password);
Example 2:
1 2RestCrowdHttpAuthenticationFactory.getAuthenticator().logout(request, response);
If there were any issues with the authentication or logout calls, an Exception will be thrown to the application.
The CrowdHttpAuthenticator manages the following:
- Authenticating an HTTP request, and setting the session with the correct attributes for other integration points of the framework.
- Invalidating an HTTP request includes removing session related attributes.
- Obtaining a principal's authenticated token from a session or browser cookie.
- Validating an existing HTTP authentication for single sign-on. If another application in the same domain has already authenticated the principal, the CrowdHttpAuthenticator will attempt to validate the existing authentication.
- Building a standard AuthenticationContext for a principal. This can be used to assure the authentication is consistent across all applications when setting validation factors of the application client.
Note both the RestCrowdHttpAuthenticationFactory and RestCrowdClientFactory manage singleton instances of the CrowdHttpAuthenticator and CrowdClient implementations respectively. You should never need to instantiate the CrowdHttpAuthenticator or CrowdClient manually.
If you are using an Inversion-of-Control / Dependency-Injection container in your web application (such as Spring) to manage your singletons, read the information about dependency injection lower down the page.
The CrowdSecurityFilter is an HTTP servlet filter that protects secured resources by verifying the session or cookie token is active and the principal has access to the requesting application. The CrowdSecurityFilter works in conjunction with the CrowdHttpAuthenticator, validating and setting various session and cookie attributes. Should the principal's token become expired or invalid due to security restrictions, the principal will be redirected to the URL provided by the crowd.properties.
Using the CrowdSecurityFilter is very straight forward, simply edit your web.xml deployment descriptor to reflect the filter and desired resource mapping:
1 2<filter> <filter-name>CrowdSecurityFilter</filter-name> <filter-class>com.atlassian.crowd.integration.http.filter.CrowdSecurityFilter</filter-class> </filter> <filter-mapping> <filter-name>CrowdSecurityFilter</filter-name> <url-pattern>/secure/*</url-pattern> </filter-mapping>
In this example, the CrowdSecurityFilter will prevent any pages on the /secure/ path from being accessed unless a valid token is found.
Should the token expire or be found invalid, the original URL will be stored in the principal's session at a String with the key of CrowdSecurityFilter.ORIGINAL_URL. This is useful because, when the principal later authenticates, the original URL and parameters can then be used as a redirect bringing the principal back to their original POST. An example of how this can be accomplished at login is shown below:
1 2RestCrowdHttpAuthenticationFactory.getAuthenticator().authenticate(request, response, username, password); // Check if principal was requesting a page that was prevented, if so, redirect. String requestingPage = (String) getSession().getAttribute(CrowdSecurityFilter.ORIGINAL_URL); if (requestingPage != null) { // redirect the principal to the requesting page response().sendRedirect(requestingPage); } else { // return the to the login page return SUCCESS; }
Using dependency injection?
If you are using a dependency injection container which manages singleton instances, rather than using the RestCrowdClientFactory and RestCrowdHttpAuthenticationFactory to manage singletons, you can wire up the objects themselves as shown in the following diagram:
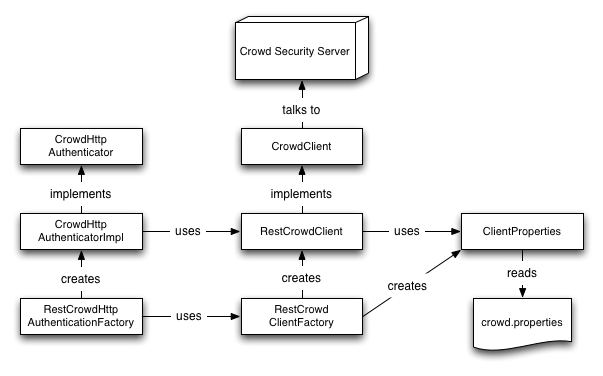
Please use EITHER dependency injection OR the factories. Using both will result in multiple instances being maintained throughout your application.
1 2<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.0.xsd"> <bean id="resourceLocator" class="com.atlassian.crowd.service.client.ClientResourceLocator"> <constructor-arg value="crowd.properties"/> </bean> <bean id="clientProperties" class="com.atlassian.crowd.service.client.ClientPropertiesImpl" factory-method="newInstanceFromResourceLocator"> <constructor-arg type="com.atlassian.crowd.service.client.ResourceLocator" ref="resourceLocator"/> </bean> <bean id="crowdClientFactory" class="com.atlassian.crowd.integration.rest.service.factory.RestCrowdClientFactory"/> <bean id="crowdClient" factory-bean="crowdClientFactory" factory-method="newInstance"> <constructor-arg ref="clientProperties"/> </bean> <bean id="validationFactorExtractor" class="com.atlassian.crowd.integration.http.util.CrowdHttpValidationFactorExtractorImpl" factory-method="getInstance"/> <bean id="tokenHelper" class="com.atlassian.crowd.integration.http.util.CrowdHttpTokenHelperImpl" factory-method="getInstance"> <constructor-arg ref="validationFactorExtractor"/> </bean> <bean id="crowdHttpAuthenticator" class="com.atlassian.crowd.integration.http.CrowdHttpAuthenticatorImpl"> <constructor-arg ref="crowdClient"/> <constructor-arg ref="clientProperties"/> <constructor-arg ref="tokenHelper"/> </bean> <bean id="crowdSecurityFilter" class="com.atlassian.crowd.integration.http.filter.CrowdSecurityFilter"> <constructor-arg ref="crowdHttpAuthenticator"/> <constructor-arg ref="clientProperties"/> </bean> </beans>
To use a Spring-injected CrowdSecurityFilter change the filter definition in your web.xml to:
1 2<filter> <filter-name>crowdSecurityFilter</filter-name> <filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.DelegatingFilterProxy</filter-class> </filter>
RELATED TOPICS
Rate this page: