Build a Jira app using a framework
Atlassian timeline for end of support for Connect
Atlassian has announced the timeline for phased end of support for Connect.
From Sep 17, 2025, only Forge apps can be submitted to the Atlassian Marketplace. All new extensibility features will be delivered only on Forge.
Have an existing Connect app? Find out how to incrementally adopt Forge from Connect.
Frameworks help to generate some of the plumbing required for your Connect app. This makes it easier to create an app and simplifies the development process. There are a range of Atlassian Connect frameworks available for different languages, frameworks and tools, but in this tutorial, we'll use one of the supported ones: Atlassian Connect Express.
Atlassian Connect Express (ACE) is the official Atlassian Connect framework for Node.js. In this tutorial, you'll set up ACE, then build a basic Jira Cloud app using it. This will be a fully fledged Atlassian Connect app, not just a web app. As a bonus, you'll be able to use it as a starting point for many of the other Jira Cloud tutorials in this documentation.
Before you begin
If you are new to Jira Cloud development, read the Getting started guide before you start this tutorial.
To complete this tutorial, you'll need the following:
- Your favorite IDE or text editor.
- A running Node.js environment (v10.0.0 or later required): download Node.js, if you don't have it already. Node.js bundles npm, which you'll also need.
- You will need to sign up for an ngrok account and store the authtoken shown on your dashboard (We will add this token to ACE later)
Install Atlassian Connect Express
In this section, you'll use npm to install Atlassian Connect Express (ACE).
-
Install the atlas-connect CLI tool by running the following command:
1 2
npm i -g atlas-connect -
Test that atlas-connect has installed correctly by checking the version:
1 2
atlas-connect -VYour terminal should show something like this:
0.6.4.
Create a Jira app using ACE
We're ready to build an app using ACE! This Jira Cloud app will be about as basic as it gets, but you'll be able to learn the fundamental steps of the process.
-
Create an app project using the
atlas-connectcommand. We're using the project namejira-getting-startedin this tutorial. Run this in any directory, except for the project directory you used for your previous app above.1 2
atlas-connect new -t jira jira-getting-startedThis command will generate the basic skeleton for your
atlassian-connect-expressenabled app, in a newjira-getting-starteddirectory:1 2
. ├── README.md ├── app.js ├── atlassian-connect.json ├── config.json ├── credentials.json.sample ├── package.json ├── private-key.pem ├── public-key.pem ├── package.json ├── public │ ├── css │ │ └── addon.css │ └── js │ └── addon.js ├── routes │ └── index.js └── views ├── hello-world.hbs ├── layout.hbs └── unauthorized.hbs -
Change to the
jira-getting-starteddirectory and install all required dependencies:1 2
npm install
That's it! You now have an Atlassian Connect app. The atlas-connect new command actually creates a simple "Hello World" dialog in your new app, which you'll see when we deploy it to Jira in the next step.
Deploy your Jira app
You have a Jira Cloud instance and you have an app. It's time to put the two together.
-
In your
jira-getting-starteddirectory, copy thecredentials.json.samplefile to a newcredentials.jsonfile. Edit thecredentials.jsonfile and update the URL, username, and password to match your Jira Cloud instance, then save it. It should look something like this:1 2
{ "hosts": { "https://your-domain.atlassian.net": { "product": "jira", "username": "youremail@domain.com", "password": "API token from id.atlassian.com" } }, "ngrok": { "authtoken": "your-ngrok-token" } } -
We're ready to deploy your app! Run the following command:
1 2
npm startThis will boot up your Express server on the default port of 3000. Here's where you'll see more benefits of using a framework, as ACE will also do the following for you:
- Create an ngrok tunnel to your local web server.
- Register your app's
atlassian-connect.json(athttp://<temp-ngrok-url>.io/atlassian-connect.json) with your host Jira Cloud instance. - Start watching for changes to your
atlassian-connect.json. If the file is modified,atlassian-connect-expresswill re-register your app with the host.
-
Finally, check that that your app is working correctly. Navigate to your Jira Cloud instance and you'll see a Hello World link in the header. Click it and you should see a page like this:
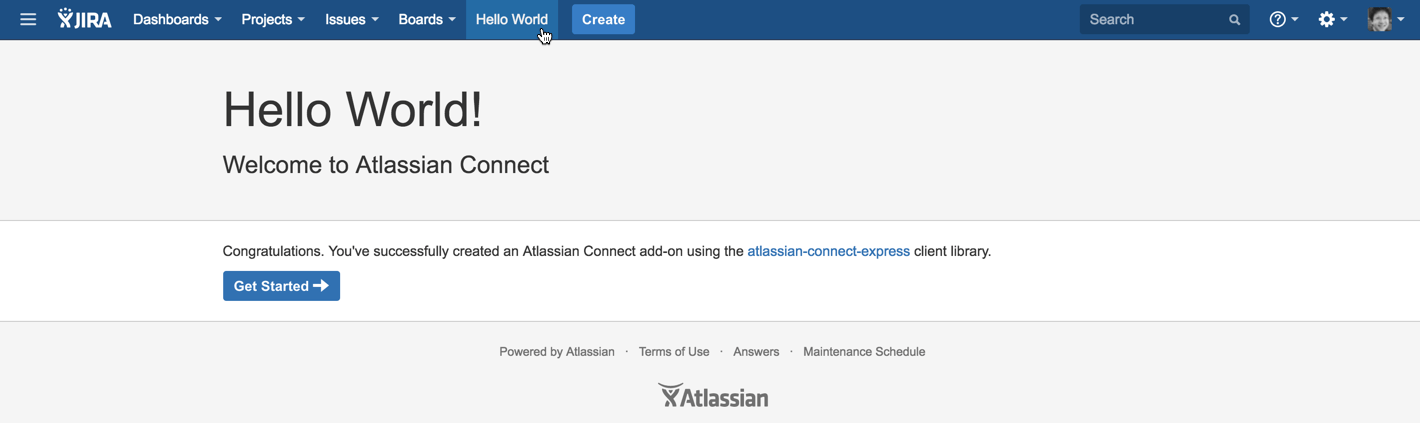
Congratulations!
Next steps
If you'd like to keep learning about app development for Jira Cloud, see the following pages:
- Learn more about the other frameworks and tools for Atlassian Connect.
- Try another tutorial. The Adding a board configuration page tutorial for Jira Software will allow you to use the basic app that you've already built and extend it to add your own UI element.
- Check out the REST API to see what is possible.
Rate this page: