objectStore (EAP)
UI components for Forge Object Store are now available as part of our Early Access Program (EAP). These components can also be used for remote object store back-ends. To start testing, sign up here.
By signing up for this Early Access Program (“EAP”), you acknowledge that use of the Forge Object Store UI Components is governed by the Atlassian Developer Terms. The Forge Object Store UI Components are considered “Early Access Materials”, as set forth in Section 10 of the Atlassian Developer Terms and is subject to applicable terms, conditions, and disclaimers.
For more details, see Forge EAP, Preview, and GA.
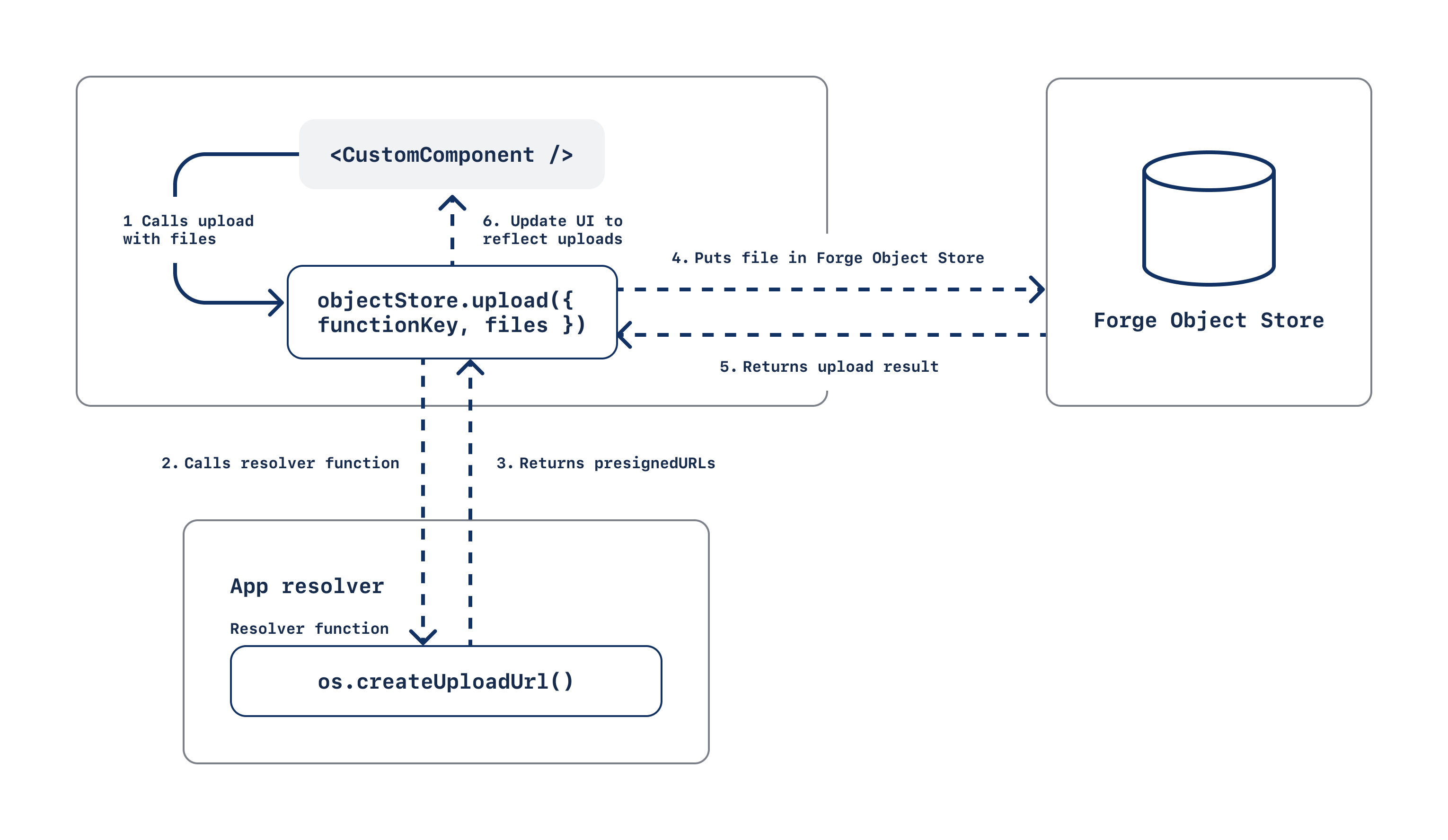
The objectStore bridge API provides methods for integrating your app's frontend with the
Forge Object Store. This diagram outlines a typical integration between the upload method and backend resolver:
Example app
We published a sample app to demonstrate the basics of implementing object storage features in a Forge app. This sample app uses the Forge Object Store as its backend and available Forge UI components for its frontend. Refer to the app's README for additional guidance on exploring and testing the code.
upload
The upload function allows you to store objects in the Forge Object Store via
pre-signed upload URLs.
Function signature
1 2const upload = ( functionKey: string, objects: Blob[] | Base64Object[] ): Promise<UploadResult[]>
Arguments
-
functionKey: A string identifier representing the resolver function that generates the pre-signed upload URLs.
The resolver function should have the following signature:
1 2
const generatePresignedUrls = async ( objectMetadata: GeneratedMetadata[], ): Promise<PresignedURLToObjectMetadataMap>Where:
1 2
type GeneratedMetadata = { /** The size of the object in bytes */ length: number; /** The checksum hash of the object content (for integrity verification) */ checksum: string; /** The type of checksum algorithm used (e.g., "SHA-256") */ checksumType: string; } type PresignedURLToObjectMetadataMap = { /** * The presigned URL generated by the backend for uploading the object. * This URL grants temporary access to upload directly to cloud storage. */ [presignedUrl: string]: { /** The unique key/path where the object will be stored */ key: string; /** The size of the object in bytes */ length: number; /** The checksum hash of the object content (for integrity verification) */ checksum: string; /** The type of checksum algorithm used (e.g., "SHA-256") */ checksumType: string; /** Optional: Time-to-live in seconds for the presigned URL (default: backend-defined) */ ttlSeconds?: number; /** Optional: Whether to overwrite existing objects with the same key (default: false) */ overwrite?: boolean; }; }; -
objects: An array of objects formatted as
BloborBase64Object.1 2
type Base64Object = { data: string; mimeType?: string; };
Returns
An UploadResult array:
1 2type UploadResult = { /** Whether the upload operation completed successfully */ success: boolean; /** The object key/path where the file was (or would have been) stored */ key: string; /** HTTP status code from the upload operation */ status?: number; /** Error message describing what went wrong (only present when success is false) */ error?: string; };
Example
The following example show how to upload multiple files to the Forge Object Store.
1 2import { objectStore } from '@forge/bridge'; async function uploadFilesFromForm() { // Get files from a file input element const fileInput = document.getElementById('fileInput') as HTMLInputElement; const files = Array.from(fileInput.files || []); // Convert File objects to Blobs (File extends Blob, so this works directly) const blobs: Blob[] = files; try { const results = await objectStore.upload({ functionKey: 'filterAndGenerateUploadUrls', // Your backend resolver function objects: blobs }); // Process results results.forEach((result) => { if (result.success) { // Handle successful upload } else { // Handle failed upload - result.error contains the error message // You can render UI feedback for this failed upload } }); } catch (error) { alert('Upload failed: ' + error.message); } }
download
The download function allows you to retrieve objects stored in the Forge Object Store via
pre-signed download URLs.
Function signature
1 2const download = ( functionKey: string, keys: string[] ): Promise<DownloadResult[]>
Arguments
-
functionKey: A string identifier representing the resolver function that generates the pre-signed download URLs.
The resolver function should have the following signature:
1 2
const generatePresignedUrls = async ( keys: string[] ): Promise<PresignedURLToObjectKeyMap>Where:
1 2
type PresignedURLToObjectKeyMap = { /** * The presigned URL generated by the backend for downloading the object. * This URL grants temporary access to download directly from cloud storage. */ [presignedUrl: string]: string; }; -
keys: An array of object keys.
Returns
An array of DownloadResult:
1 2type DownloadResult = { /** Whether the download operation completed successfully */ success: boolean; /** The object key/path of the file */ key: string; /** The object */ blob: Blob; /** HTTP status code from the download operation */ status?: number; /** Error message describing what went wrong (only present when success is false) */ error?: string; };
Example
The following example shows how to download multiple files from the Forge Object Store.
1 2import { objectStore } from '@forge/bridge'; async function downloadMultipleFiles() { const fileKeys = [ 'shared/documents/invoice-001.pdf', 'shared/documents/invoice-002.pdf', 'shared/documents/invoice-003.pdf' ]; try { const results = await objectStore.download({ functionKey: 'filterAndGenerateDownloadUrls', keys: fileKeys }); // Process each result results.forEach((result) => { if (result.success && result.blob) { // Handle successful download } else { // Handle failed download } }); } catch (error) { // Handle error } }
getMetadata
The getMetadata function allows you to
retrieve the metadata of an object stored in the Forge Object Store.
Function signature
1 2const getMetadata = ( functionKey: string, keys: string[] ): Promise<GetMetadataResult[]>
Arguments
- functionKey: A string identifier representing the resolver function that requests metadata from the Object Store.
- keys: An array of object keys.
Returns
An array of GetMetadataResult:
1 2type GetMetadataResult = { /** The object key/path in storage that was queried */ key: string; /** SHA-256 checksum hash of the object content */ checksum?: string; /** Size of the object in bytes */ size?: number; /** ISO 8601 timestamp of when the object was created */ createdAt?: string; /** Version identifier for the object (if versioning is enabled) */ currentVersion?: string; /** Error message describing what went wrong */ error?: string; };
Example
The following example shows how to retrieve the metadata of multiple objects stored in the Forge Object Store.
1 2import { objectStore } from '@forge/bridge'; const fileKeys = [ 'shared/documents/report-2025.pdf', 'shared/documents/invoice-001.pdf', 'shared/images/logo.png', 'shared/videos/tutorial.mp4', 'shared/data/export.json' ]; async function getMultipleFileMetadata(fileKeys: string[]) { try { const results = await objectStore.getMetadata({ functionKey: 'getObjectMetadata', keys: fileKeys }); return results; } catch (error) { throw error; } }
delete
The delete function allows you to delete objects from Forge Object Store.
Function signature
1 2const delete = ( functionKey: string, keys: string[] ): Promise<void>
Arguments
- functionKey: A string identifier representing the resolver function that requests the deletion of objects from the Object Store.
- keys: An array of object keys.
Example
The following example shows how to delete multiple objects from Forge Object Store.
1 2import { objectStore } from '@forge/bridge'; const fileKeys = [ 'shared/documents/report-2025.pdf', 'shared/documents/invoice-001.pdf', 'shared/images/logo.png', 'shared/videos/tutorial.mp4', 'shared/data/export.json' ]; async function deleteMultipleFiles(fileKeys: string[]) { try { const results = await objectStore.delete({ functionKey: 'deleteObject', keys: fileKeys }); return results; } catch (error) { throw error; } }
Rate this page: