- ADF renderer
- Badge
- Box
- Button
- Button group
- Calendar
- Chart - Bar
- Chart - Donut
- Chart - Horizontal bar
- Chart - Horizontal stack bar
- Chart - Line
- Chart - Pie
- Chart - Stack bar
- Checkbox
- Checkbox group
- Code
- Code block
- Comment
- Comment editor
- Chromeless editor
- Date picker
- Dynamic table
- Empty state
- File card (EAP)
- File picker (EAP)
- Form
- Frame
- Heading
- Icon
- Image
- Inline
- Inline edit
- Link
- List
- Lozenge
- Modal
- Popup
- Pressable
- Progress bar
- Progress tracker
- Radio
- Radio group
- Range
- Section message
- Select
- Spinner
- Stack
- Tabs
- Tag
- Tag group
- Text
- Text area
- Text field
- Time picker
- Tile (Preview)
- Toggle
- Tooltip
- User
- User group
- User picker
- XCSS
ADF renderer
To add the AdfRenderer component to your app:
1 2import { AdfRenderer } from "@forge/react";
Description
The AdfRenderer component provides a way to render a valid ADF document, using the same renderer that Atlassian uses internally to render ADF content in Confluence pages, Jira work items, and so on.
It allows you to replace node types that are unsupported in the context of a Forge app with replacement content, or remove them entirely.
See Atlassian Document Format for information on valid nodes.
This component uses @atlaskit/renderer under the hood.
Visit Renderer editor for a comprehensive list of different ADF document examples.
Accessibility considerations
When using the replaceUnsupportedNode prop you will need to ensure that any content is replaced with accessible content.
This content needs to be clear to the user it has been replaced. Including an explanation as to why the content is replaced can also be useful.
Read more about Readable content (as per WCAG success criterion)
This helps users who use:
- Screen readers
- Braille display
- Text-to-speech technology
Props
| Name | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
document | DocNode | Yes | An ADF document to render |
replaceUnsupportedNode | Visitor | No | A function to determine behaviour for handling unsupported nodes:
|
See @atlaskit/renderer for the full list of props supported by the underlying component.
Unsupported node types
| Node type | Support | Details |
|---|---|---|
media | Partial | Only supports media hosted by Atlassian when used in a Confluence macro module. You can identify Atlassian hosted `media` nodes as they have an attrs.id property, instead of attrs.url |
emoji | Partial | Only standard Unicode emoji are supported, not custom user-provided emoji |
|
| None | All types of Forge macros are supported, except for Forge bodied macros; see Rendering a UI Kit bodied macro for the new EAP feature. However, core Confluence macros and Connect macros are not supported. |
Examples
Rendering a UI Kit bodied macro
The AdfRenderer component now supports rendering embedded Forge Custom UI and UI Kit apps as an Early Access Program (EAP). To start testing this feature, sign up using this form.
By signing up for this Early Access Program (“EAP”), you acknowledge that use of the Forge embedded macros is governed by the Atlassian Developer Terms. Forge embedded macros are considered “Early Access Materials”, as set forth in Section 12 of the Atlassian Developer Terms and is subject to applicable terms, conditions, and disclaimers.
APIs and features under EAP are unsupported and subject to change without notice. APIs and features under EAP are not recommended for use in production environments.
For more details, see Forge EAP, Preview, and GA.
This demonstrates how to render the contents of a UI Kit bodied macro, including bodied macros that contain embedded UI Kit or Custom UI Forge apps. For Custom UI bodied macros, see createAdfRendererIframeProps.
Prerequisites:
-
Your app must be a Confluence bodied macro with layout:bodied enabled in the macro module properties of the manifest file.
-
This approach is for UI Kit apps only. For Custom UI, use
view.createAdfRendererIframePropsinstead.
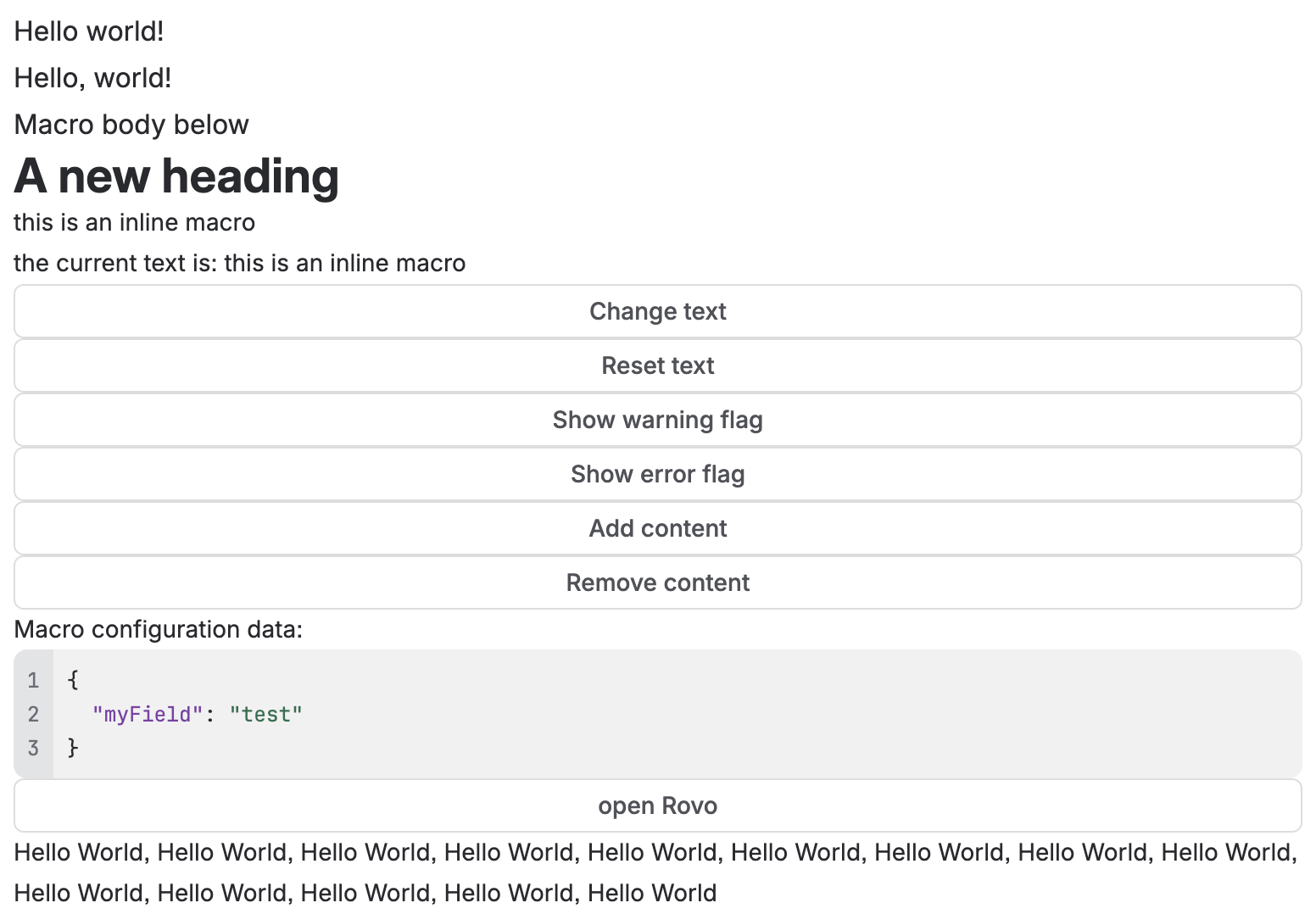
1 2import React from "react"; import ForgeReconciler, { Text, useProductContext, AdfRenderer, } from "@forge/react"; const App = () => { const context = useProductContext(); const macroBody = context?.extension?.macro?.body; return ( <> <Text>Hello world!</Text> <Text>Macro body below</Text> {macroBody ? ( <AdfRenderer document={macroBody} /> ) : ( <Text>loading macro content...</Text> )} <Text>Macro body above</Text> </> ); }; ForgeReconciler.render( <React.StrictMode> <App /> </React.StrictMode> );
If the UI Kit bodied macro contains multiple Forge embedded macro apps, you can optionally split it up and pass it to multiple <AdfRenderer document={macroBody} /> instances.
See limitations and supported bridge methods for rendering embedded UI Kit or Custom UI Forge apps.
Basic text rendering
This demonstrates how a simple ADF document is rendered.

1 2import { AdfRenderer } from "@forge/react"; export const AdfRendererBasicExample = () => { const simpleDocumentToRender = { type: "doc", version: 1, content: [ { type: "paragraph", content: [ { type: "text", text: "This is a simple text example", }, ], }, ], }; return <AdfRenderer document={simpleDocumentToRender} />; };
Rendering unsupported content
This demonstrates how unsupported content might render by default, without any explicit replacement logic defined.

1 2import { AdfRenderer } from "@forge/react"; export const AdfRendererUnsupportedExample = () => { const simpleDocumentToRender = { type: "doc", version: 1, content: [ { type: "paragraph", content: [ { type: "emoji", attrs: { shortName: ":custom-emoji-hello:", id: "1e35b00f-cb17-4d28-91a5-ad38700715ae", text: ":hello!:", }, }, ], }, ], }; return <AdfRenderer document={simpleDocumentToRender} />; };
Replacing unsupported content
This demonstrates a simple replacement function that just replaces unsupported content with a paragraph.

1 2import { AdfRenderer } from "@forge/react"; export const AdfRendererUnsupportedContentExample = () => { const replaceUnsupportedNode = (node) => { return { type: "paragraph", content: [ { type: "text", text: `Unsupported content: ${node.type}`, }, ], }; }; const simpleDocumentToRender = { type: "doc", version: 1, content: [ { type: "paragraph", content: [ { type: "emoji", attrs: { shortName: ":custom-emoji-hello:", id: "1e35b00f-cb17-4d28-91a5-ad38700715ae", text: ":hello!:", }, }, ], }, ], }; return ( <AdfRenderer document={simpleDocumentToRender} replaceUnsupportedNode={replaceUnsupportedNode} /> ); };
Replacing multiple content types
This demonstrates a more complex replacement function that either replaces content, removes it, and or leaves it as-is, depending on the node type.

1 2import { AdfRenderer } from "@forge/react"; export const AdfRendererMultipleContentTypesExample = () => { const replaceUnsupportedNode = (node) => { if (node.type.toLowerCase().includes("extension")) { // Show a message for all extension node types return { type: "paragraph", content: [ { type: "text", text: "Unsupported macro", }, ], }; } else if (node.type === "emoji") { // Show the emoji's default textual representation as-is return undefined; } // Hide everything else return false; }; const simpleDocumentToRender = { type: "doc", version: 1, content: [ { type: "paragraph", content: [ { type: "emoji", attrs: { shortName: ":custom-emoji-hello:", id: "1e35b00f-cb17-4d28-91a5-ad38700715ae", text: ":hello!:", }, }, { type: "bodiedExtension", attrs: { extensionType: "com.atlassian.fabric", extensionKey: "clock", }, content: [ { type: "paragraph", content: [ { type: "text", text: "This is the default content of the extension", }, ], }, ], }, ], }, ], }; return ( <AdfRenderer document={simpleDocumentToRender} replaceUnsupportedNode={replaceUnsupportedNode} /> ); };
Rate this page: