Automate Jira using triggers
This tutorial describes how to create a Forge app and install it in a Jira Cloud site. The app responds to issue created events in Jira and adds a comment to the created issue.
Forge invocation limits also apply to web triggers (scheduled and unscheduled). Refer to our platform invocation limits for more details.
You'll learn about Atlassian app events, the Runtime API, and tunneling.
Before you begin
To complete this tutorial, you need the latest version of Forge CLI. To update your CLI version, run npm install -g @forge/cli@latest
on the command line.
We recommend that you complete all the steps in Getting started so that you’re familiar with the Forge development process.
Set up a cloud developer site
An Atlassian cloud developer site lets you install and test your app on Atlassian apps including Confluence and Jira. If you don't have one yet, set it up now:
- Go to http://go.atlassian.com/cloud-dev and create a site using the email address associated with your Atlassian account.
- Once your site is ready, log in and complete the setup wizard.
You can install your app to multiple Atlassian sites. However, app data won't be shared between separate Atlassian apps, sites, or Forge environments.
The limits on the numbers of users you can create are as follows:
- Confluence: 5 users
- Jira Service Management: 1 agent
- Jira Software and Jira Work Management: 5 users
Step 1: Create your app
Create an app based on the Hello world template.
-
Navigate to the directory where you want to create the app.
-
Create your app by running:
1 2
forge create -
Enter a name for the app. For example, comment-issue-app.
-
Select
Show All, and thenTriggers and Validatorscategory. -
Select the
product-triggertemplate from the list. -
Open the app directory to see the app files.
Step 2: Define app permissions
Your app needs to define the OAuth 2.0 scopes to use when calling the Jira Cloud REST API.
Add the Required Scopes
-
read:jira-work: Required for app handlingavi:jira:created:issuetriggers. -
write:jira-work: Required OAuth scope for the Add comment API which you'll use in the tutorial.
-
Open the
manifest.ymlfile. -
Add a new permission with the scopes
read:jira-workandwrite:jira-work.1 2
permissions: scopes: - read:jira-work - write:jira-work
See Scopes for detailed information about the available scopes.
Your manifest.yml file should look like the following, with your value for the app ID.
1 2permissions: scopes: - read:jira-work - write:jira-work modules: trigger: - key: issue-created-event function: main events: - avi:jira:created:issue function: - key: main handler: index.run app: id: '<your-app-id>'
The code above creates a trigger module that responds to the Atlassian app event avi:jira:created:issue.
This event happens when an issue is created in the Jira site where the app is installed.
When the event occurs, the main function is triggered.
Step 3: Use a tunnel to test the app
The main function is called when a new Jira issue is created. This function is located in the
src/index.js file, which logs this message:
1 2export async function run(event, context) { console.log('Hello World!'); }
You’ll use the tunnel command from the Forge CLI to run your function locally, allowing you to quickly check your code changes. When a trigger is received by Forge (in the cloud), the function running locally is invoked.
-
In your app's top-level directory, deploy your app by running:
1 2
forge deploy -
Install the app on your site and authorize it by following the prompts after running the command:
1 2
forge install- Select
Jiraas the Atlassian app. - Enter the URL for your Atlassian site. For example,
your-domain.atlassian.net. - Authorize your app using the URL displayed.
- Select
-
Start a tunnel by running:
1 2
forge tunnelThis enables you to test your app without having to deploy it after each change.
The tunnel works for changes to the code, not for configuration changes to the
manifest.ymlfile. If you change the app configuration in themanifest.yml, you need to redeploy the app (forge deploy), and then restart the tunnel (forge tunnel). -
Create a new issue in your Jira site. Make sure to create the issue in a project where you can view and comment on issues.
-
Verify
Hello World!appears in your tunnel.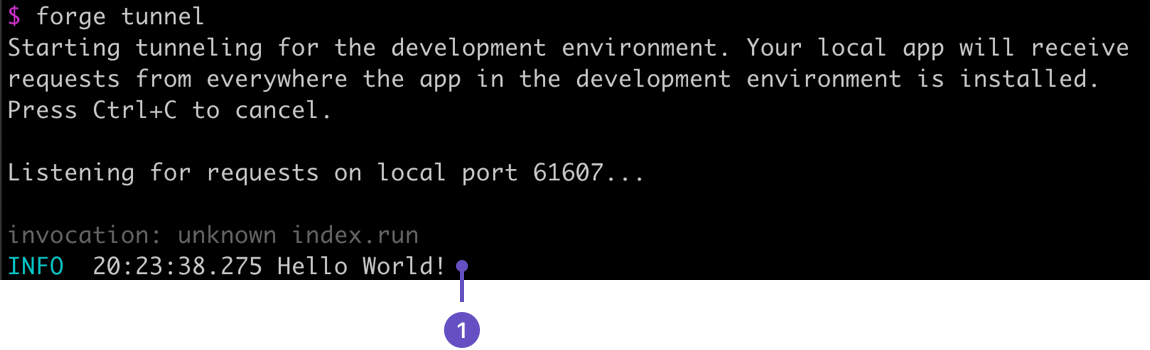
Step 4: Use the Jira REST API to add a comment
In Step 3, we demonstrated how creating a new issue invoked the run method in src/index.js.
In this step, you’ll create a function that uses the Runtime API to add a comment to the new issue in response to the issue created event.
-
In the app’s top-level directory, install the npm package dependency for the Runtime API by running:
1 2
npm install @forge/api -
Open the
src/index.jsfile. -
Import the Runtime API by adding the following to the top of the file.
1 2
import api, { route } from "@forge/api"; -
Create the
addCommentfunction below therunfunction:1 2
async function addComment(issueIdOrKey, message) { /** * @issueIdOrKey - the Jira issueId number or key for the issue that this function will try to add * a comment to (as per the Jira Rest API) * @message {string} - the message that will appear in the comment * * @example addComment('10050', 'Hello world') */ // You'll come back to this later const requestUrl = route`https`; const body = { }; // Use the Forge Runtime API to fetch data from an HTTP server using your (the app developer) Authorization header let response = await api.asApp().requestJira(requestUrl, { method: "POST", headers: { "Content-Type": "application/json" }, body: JSON.stringify(body) }); // Error checking: the Jira issue comment Rest API returns a 201 if the request is successful if (response.status !== 201) { console.log(response.status); throw `Unable to add comment to issueId ${issueIdOrKey} Status: ${response.status}.`; } return response.json(); } -
Modify the
runfunction to call theaddCommentfunction:1 2
export async function run(event, context) { const response = await addComment(event.issue.id, "Hello World! It's the Comment Issue app."); console.log(`Response: ${JSON.stringify(response)}`); } -
Finally, complete the
requestUrlandbodydefinition in theaddCommentfunction:1 2
// See https://developer.atlassian.com/cloud/jira/platform/rest/v3/#api-rest-api-3-issue-issueIdOrKey-comment-post // IssueIDOrKey: The ID or key of the issue. const requestUrl = route`/rest/api/3/issue/${issueIdOrKey}/comment`; const body = { "body": { "type": "doc", "version": 1, "content": [ { "type": "paragraph", "content": [ { "text": message, "type": "text" } ] } ] } };- The
requestUrluses the Jira cloud REST API with path/rest/api/3/issue/{issueIdOrKey}/comment. - The body is the comment message in Atlassian Document Format.
- The
-
Start your tunnel if it’s not still running from step 4.
-
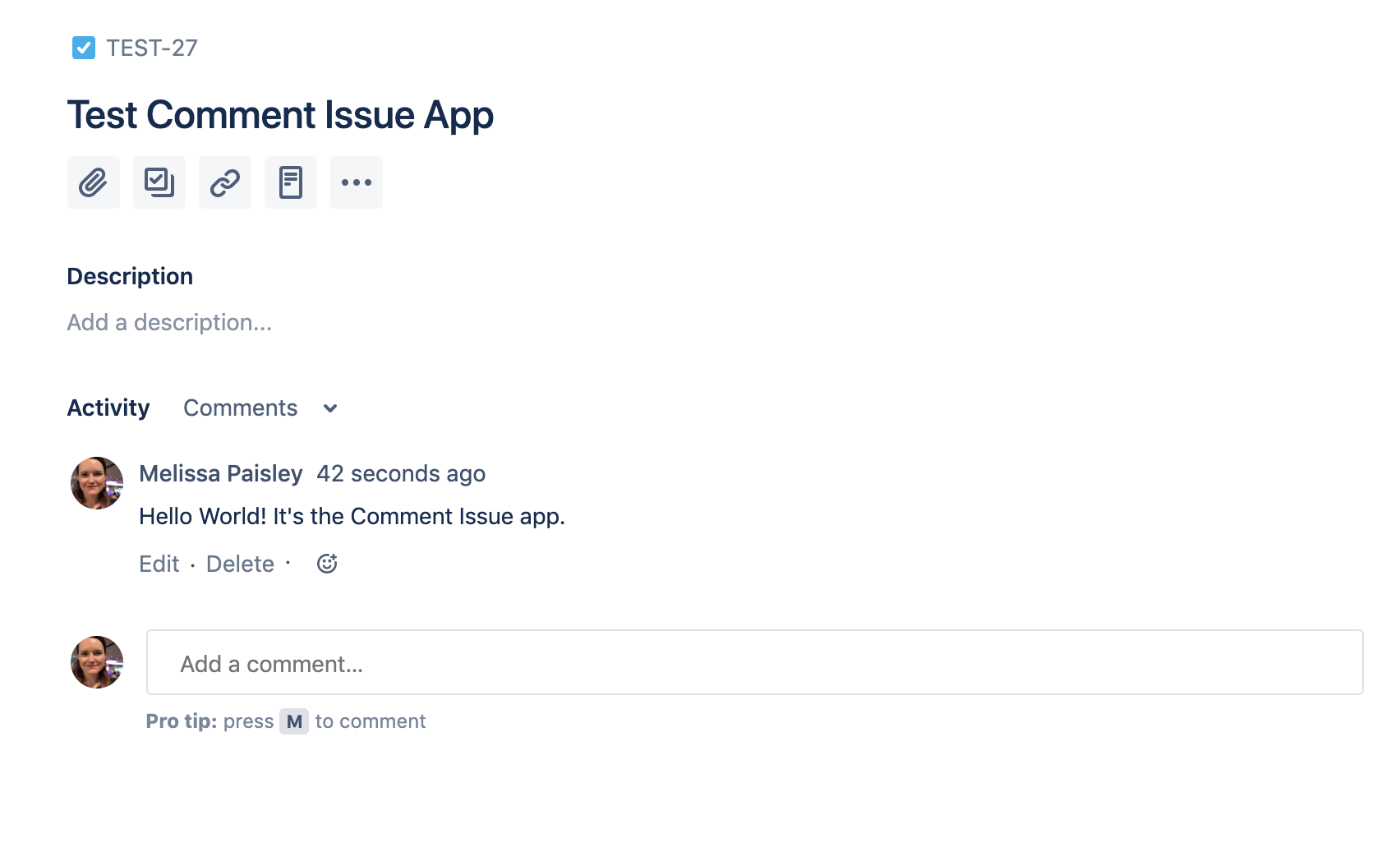
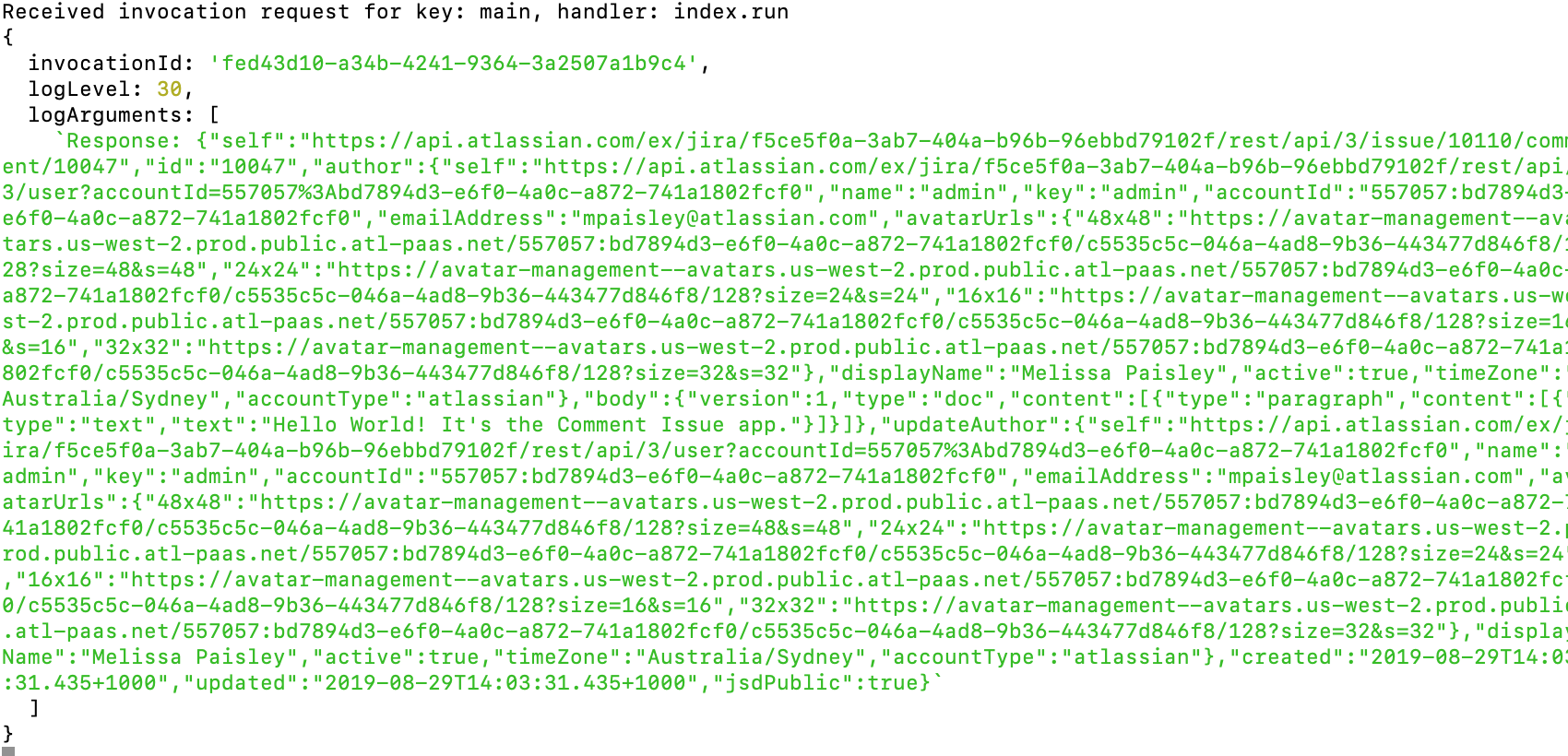
Create an issue in the site where you installed your app, and verify the following:
- You receive a response message in the tunnel.
- The issue you created now has a comment.

- You receive a response message in the tunnel.
Your index.js should look like the following:
1 2import api, { route } from "@forge/api"; export async function run(event, context) { const response = await addComment(event.issue.id, "Hello World! It's the Comment Issue app."); console.log(`Response: ${JSON.stringify(response)}`); } async function addComment(issueIdOrKey, message) { /** * @issueIdOrKey - the Jira issueId number or key for the issue that this function will try to add * a comment to (as per the Jira Rest API) * @message {string} - the message that will appear in the comment * * @example addComment('10050', 'Hello world') */ // See https://developer.atlassian.com/cloud/jira/platform/rest/v3/#api-rest-api-3-issue-issueIdOrKey-comment-post const requestUrl = route`/rest/api/3/issue/${issueIdOrKey}/comment`; const body = { "body": { "type": "doc", "version": 1, "content": [ { "type": "paragraph", "content": [ { "text": message, "type": "text" } ] } ] } }; // Use the Forge Runtime API to fetch data from an HTTP server using your (the app developer) Authorization header let response = await api.asApp().requestJira(requestUrl, { method: "POST", headers: { "Content-Type": "application/json" }, body: JSON.stringify(body) }); // Error checking: the Jira issue comment Rest API returns a 201 if the request is successful if (response.status !== 201) { console.log(response.status); throw `Unable to add comment to issueId ${issueIdOrKey} Status: ${response.status}.`; } return response.json(); }
Event payload
The event payload contains data about the event, as well as the site the event occurred in. In this tutorial, you extract the issue ID from the payload, and use it when making your API call to ensure the comment is added to the correct issue.
See Atlassian app events to learn more about the format of the event payload.
Step 5: Deploy your app
In step 4, you made changes to your app using the Forge Runtime API, and then tested the changes using a tunnel. Now that your app is working, deploy the changes so the app continues to work when the tunnel is closed.
-
Close the tunnel by pressing Ctrl+C.
-
Deploy the app by running:
1 2
forge deployOnce the app is deployed you’ll see a message as follows:
1 2
✔ Deployed Deployed comment-issue-app to the development environment. -
Create an issue in the site the app is installed in, and confirm that the comment is created.
Great work! You’ve created a Forge app that:
- Detects when an issue is created in the site where it is installed.
- Responds by adding a comment to the issue.
You’ve tested the app using tunneling, deployed it to the default development environment, and installed it into a Jira Cloud site.
Next steps
Continue to one of the other tutorials or look through the reference pages to learn more.
- See the reference pages to learn what else you can do with what you’ve learned.
Rate this page: