Part 1: Build a Bitbucket hello world app
This tutorial will walk you through creating a sample Forge app for Bitbucket. There are three parts to the tutorial:
- This page: describes creating, changing, and installing a simple hello world app. The focus is on learning the CLI commands needed to work with apps.
- Call a Bitbucket API: describes how to make API calls to the Bitbucket REST API.
- Change the frontend with UI Kit: describes how to use UI Kit components.
We recommend you work through all three parts to get a good understanding of how to develop apps with Forge.
Before you begin
To complete this tutorial, you need to do complete Getting started before working through this page.
Set up a shared team workspace
For Bitbucket apps you need to join or create a shared Bitbucket team workspace (as Forge apps are not supported on personal workspaces). If you don't have a Bitbucket workspace, see the references below for related instructions:
A free Bitbucket team space can have up to 5 users.
Forge apps can't be viewed by anonymous users. When testing a Forge app, you should be logged in to Bitbucket.
Create your app
Create an app based on the Bitbucket repository code overview card template. You can view the completed app code in the Bitbucket Forge Hello World repository.
When you create a new app, Forge will prompt you to set a default environment. In this
tutorial we use the development environment as our default.
Learn more about staging and production environments.
-
Navigate to the directory where you want to create the app. A new subdirectory with the app’s name will be created there.
-
Create your app by running:
1 2
forge create -
Enter a name for your app (up to 50 characters). For example, hello-world-app.
-
Select Bitbucket as the context.
-
Select the UI Kit category.
-
Select the bitbucket-repository-code-overview-card template.
-
Change to the app subdirectory to see the app files:
1 2
cd hello-world-app
bitbucket-repository-code-overview-card template
The app we'll create will display a card panel on all Bitbucket repository source pages and will have a function that provides the contents of the panel.
The bitbucket-repository-code-overview-card template uses Node.js and has the following structure:
1 2hello-world-app ├── README.md ├── manifest.yml ├── package-lock.json ├── package.json └── src ├── frontend │ └── index.jsx ├── index.js └── resolvers └── index.js
Let’s have a look at what these files are:
manifest.yml: Describes your app. This file contains the name and ID of the app, the app permissions, and the modules the app uses. To learn more about themanifest.ymlfile, see Forge manifest documentation.package.json: The app’s Node.js metadata. See the Node documentation for more information.package-lock.json: Records the version of the app’s dependencies.README.md: Information about the app. We recommend updating this as you change the behavior of the app.src/frontend/index.jsx: Where you write the application with which the user interacts directly.src/resolvers/index.js: Where you write the resolver function definitions. To learn more about resolvers, see the Custom UI Resolver documentation.
You can manage, monitor and distribute your apps in the developer console.
Change the panel title
This app displays content in a Bitbucket repository card panel using the bitbucket:repoCodeOverviewCard
module. Bitbucket shows the title of the bitbucket:repoCodeOverviewCard as the panel's heading.
Let's change the title to include your name.
- In the app’s top-level directory, open the
manifest.ymlfile. - Find the
titleentry under thebitbucket:repoCodeOverviewCardmodule. - Change the value of
titletoForge app for <your name>. For example, Forge app for Mia.
Your manifest.yml file should look like the following, with your values for the title and app ID:
1 2modules: bitbucket:repoCodeOverviewCard: - key: hello-world-app-hello-world-repository-code-overview-card resource: main resolver: function: resolver render: native title: Forge app for Mia function: - key: resolver handler: index.handler resources: - key: main path: src/frontend/index.jsx app: id: '<your app id>'
Install your app
To use your app, it must be installed onto a Bitbucket workspace. The
forge deploy command builds, compiles, and deploys your code; it'll also report any compilation errors.
The forge install command then installs the deployed app onto a Bitbucket workspace with the required API access.
You must run the forge deploy command before forge install because an installation
links your deployed app to a Bitbucket workspace.
-
Navigate to the app's top-level directory and deploy your app by running:
1 2
forge deploy -
Install your app by running:
1 2
forge install -
Select Bitbucket using the arrow keys and press the enter key.
-
Enter the URL for your workspace. For example, https://bitbucket.org/example-workspace/.
Forge apps are not supported on personal workspaces. If you install an app to a personal workspace, you will get an insufficient permissions error. See set up a shared team workspace.
Once the successful installation message appears, your app is installed and ready to use on the specified workspace.
You can verify the app installation in the specified workspace by navigating to Installed apps
in workspace settings. Your installed Forge app will be visible under the Forge apps section.
If the app is distributed,
you can access the direct distribution link for the app via the Manage link next to it,
which allows you to check the app details and manage the app installation, including deleting the app.
Otherwise, you can always delete your app from the workspace by running the forge uninstall command from your Forge CLI.
Running the forge install command only installs your app into the selected Atlassian app.
To install into multiple Atlassian apps, repeat these steps again, selecting another Atlassian app each time.
You must run forge deploy before running forge install in any of the Forge environments.
View your app
With your app installed, it’s time to see the app on a repository.
- Create a new Bitbucket repository if you haven't already. See Creating a repository for more information.
- Navigate to the source page in the repository. Your app should appear in the bottom of the Repository details pane on the right:
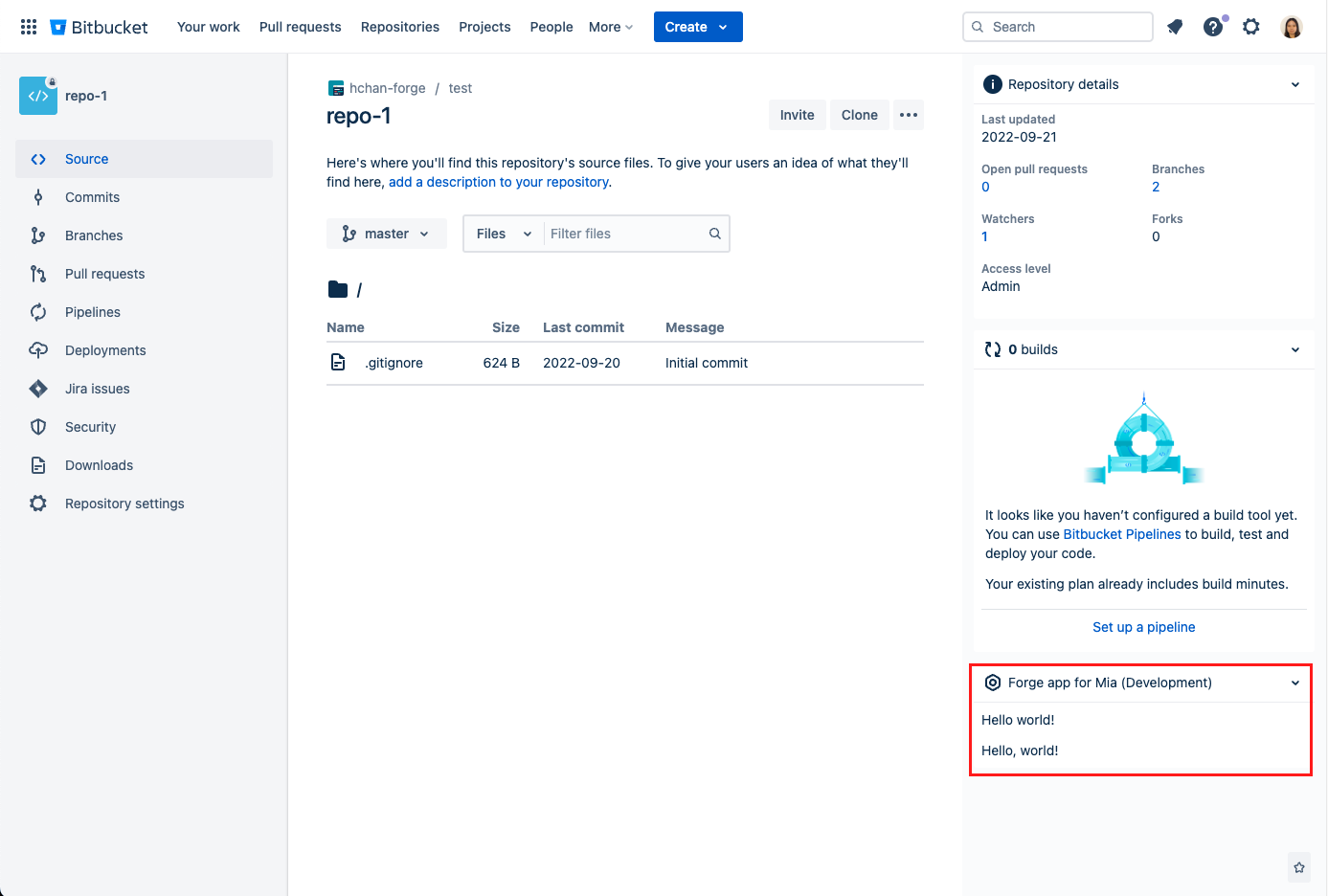
- To view new changes in your app, run
forge deployagain, or runforge tunnel. This is explained fully in the next section.
While your app is deployed to either a development or staging environment, (development) or
(staging) will appear in your app title. This suffix is removed once you've
deployed your app to production.
Deploy app changes
Once your app is installed, it will automatically pick up all minor app deployments
so you don't need to run the forge install command again. Minor deployments are changes
that don't modify app permissions in the manifest.yml file. You can deploy the changes onto your
developer site or Bitbucket workspace by using one of two methods:
- Manually, by running the
forge deploycommand. - Automatically, by running the
forge tunnelcommand.
Once your app is installed, changes in the manifest are picked up automatically after running forge deploy.
However, due to the eventually-consistent nature of our system, you may need to wait up to 5 minutes
for changes in the manifest to be reflected in the Atlassian app.
Tunneling runs your app code locally on your machine via the Forge CLI and Cloudflare. It allows you to speed up development by avoiding the need to redeploy each code change, and by seeing each invocation as it executes. The Forge tunnel works similarly to hot reloading, so any changes you make to your app code can be viewed on your Atlassian site or Bitbucket workspace without losing the current app state. You don’t need to run any other commands; you only need to refresh the page.
Once you've completed testing your app changes using forge tunnel command, please remember to redeploy your app using the forge deploy command.
- You can start tunneling by running:
1 2forge tunnel
You should see output similar to:
1 2Tunnel redirects requests you make to your local machine. This occurs for any Atlassian site where your app is installed in the specific development environment. You will not see requests from other users. Press Ctrl+C to cancel. === Running forge lint... No issues found. === Bundling code... ✔ Functions bundled. ✔ Resources bundled. Listening for requests...
You can now automatically deploy changes to your codebase and install packages, while tunneling. These changes appear on the Atlassian site or Bitbucket workspace where your app is installed.
- When you are ready to close the tunnel, press Control + C.
The forge tunnel command only forwards traffic when the user (in Jira, Confluence, Jira
Service Management, or Bitbucket) matches the Forge CLI user. For security reasons, you can’t see the traffic
of other users.
For important caveats on how forge tunnel works, see
Tunneling.
Next step
In the next tutorial, you'll learn how to make API calls to Bitbucket using Forge. This tutorial
uses the forge tunnel, so make sure you are familiar with using this command.
Developing for Atlassian Government Cloud
This content is written with standard cloud development in mind. To learn about developing for Atlassian Government Cloud, go to our Atlassian Government Cloud developer portal.
Rate this page:
