Prepare to build your first Forge app
Welcome to developing with the Forge platform for Atlassian cloud apps. Work through the steps below to set up your development environment. To get started using Forge, you’ll install the CLI, log in with an Atlassian API token, and create an Atlassian developer site that has Confluence and all of the Jira applications installed.
After setting up, you'll go through a three-part tutorial to create a simple hello world app for Bitbucket, Confluence, Jira, or Jira Service Management.
For more of an introduction to creating and managing an app with the Forge CLI, check out our Atlassian Developer YouTube channel.
Before you begin
Forge apps are written in JavaScript so you'll need to be familiar with JavaScript. It's also helpful to be familiar with React.
The content on this page is written with standard cloud development in mind. To learn about developing for Atlassian Government Cloud, go to our Atlassian Government Cloud developer portal.
Set up Node.js
The Forge CLI requires a fully supported LTS release of Node.js installed; namely, versions 20.x, 22.x or 24.x. Follow the Node.js setup instructions specific to your operating system below:
In this video, we'll walk you through installing the Atlassian Forge CLI on your Mac. Also, you'll find step-by-step written instructions on this page if you prefer to follow along at your own pace
Forge developers on macOS should use Node Version Manager (nvm) to configure the environment.
-
Install nvm.
-
Select the latest Node.js LTS release by running the following in the terminal:
1 2
nvm install --lts nvm use --lts
If nvm command doesn't work, try restarting the terminal.
-
Check your Node.js version, run the following in the terminal:
1 2
node --version
Which outputs your node version.
(Optional) Node.js installer
Skip this step if you have successfully completed Set up Node.js section.
You can install Node.js using the macOS installer, however this results in permission errors when working with the Forge CLI. If you must use the installer, you'll need to enable unsafe permissions to use the Forge global package when installing Node.js using this method.
-
Download the LTS installer from Node.js.
-
Install the package.
-
Configure npm, permitting unsafe permissions:
1 2
npm config set unsafe-perm true
Hello world CLI overview
After installing the Forge CLI, follow the prompts in the terminal to build a hello world app. For a complete explanation of each step, continue reading along with the documentation.
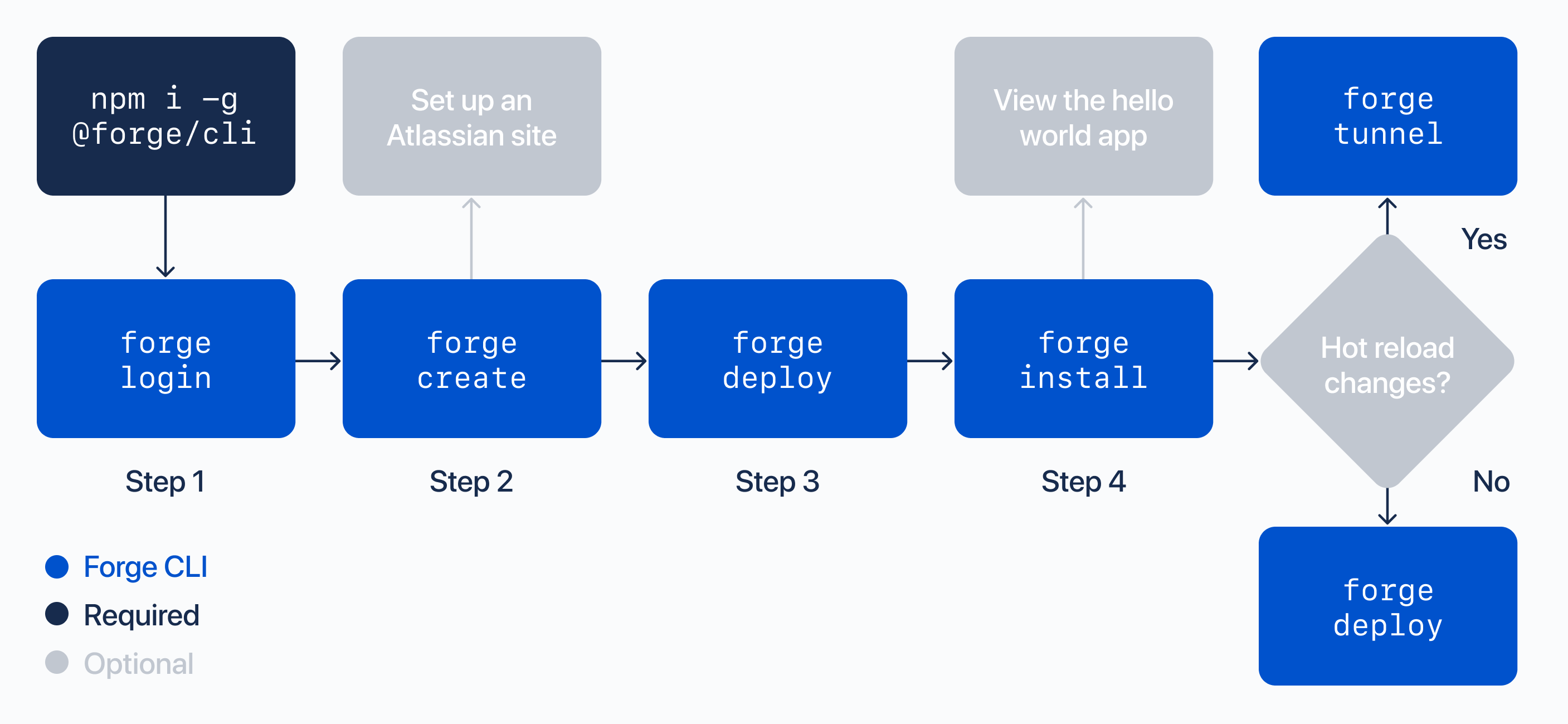
Install the Forge CLI
Install the Forge CLI using npm. You’ll install the CLI globally so that the commands can be run across your system.
Do not install forge with root privileges. In case that has been done, you might need to uninstall forge.
This can be done using the command in mac (or similar in other OS)
1 2sudo rm -rf ~/Library/Preferences/@forge
-
Install the Forge CLI globally by running:
1 2
npm install -g @forge/cli -
Verify that the CLI is installed correctly by running:
1 2
forge --version
You should see a version number reported in the terminal. If a version number is not shown, then the installation failed. Repeat step 1 and look for errors reported in the terminal.
With the CLI installed, view the complete list of Forge commands by running forge --help.
Log in with an Atlassian API token
Create or use an existing Atlassian API token to log in to the CLI. The CLI uses your token when running commands.
- Go to https://id.atlassian.com/manage/api-tokens.
- Click Create API token.
- Enter a label to describe your API token. For example, forge-api-token.
- Click Create.
- Click Copy to clipboard and close the dialog.
Log in to the Forge CLI to start using Forge commands.
Do not use sudo or root user when running forge. Doing so may cause issues with file permissions and ownership,
potentially leading Forge CLI not functioning properly when run by a non-privileged user.
-
Start the process by running:
1 2
forge login -
You'll be asked whether to allow Forge to collect usage analytics data:
1 2
Allow Forge to collect CLI usage and error reporting information?Answering
Yeswill allow Forge to collect data about your app's deployments and installations (including error data). This, in turn, helps us monitor Forge's overall performance and reliability. The collected data also helps us make better decisions on improving Forge's feature set and performance.For information about how Atlassian collects and handles your data, read our Privacy Policy.
-
Enter the email address associated with your Atlassian account.
-
Enter your Atlassian API token. You copied this to the clipboard in step 5.
You will see a message similar to this confirming you are logged in:
1 2✔ Logged in as Mia Krystof
If you get some permission error, this might be due to installation of forge with root permissions.
Try removing forge installation and try to install without root permissions.
The Forge CLI uses your operating system's keychain to securely store your login details.
Any command after forge login that requires authentication will read your credentials
from the keychain. When this occurs, your keychain may prompt you for access; approve it to allow the
CLI to run the command.
On Linux, you'll need libsecret installed to perform this step.
Using environment variables to login
If a keychain isn't available, you can store your login email and token through the environment variables FORGE_EMAIL and FORGE_API_TOKEN, respectively. In continuous integration environments, you can store these environment variables as secrets for your builds. For more information, read our tutorial on setting up continuous delivery for Forge apps.
Otherwise, you can also set environment variables manually:
1 2read FORGE_EMAIL # Enter email read -s FORGE_API_TOKEN # Enter API token (will not be displayed) export FORGE_EMAIL FORGE_API_TOKEN
This applies to all commands that require forge login to be run first.
- If you are using environment variables instead of the keychain, do not use the
forge logincommand and proceed directly to utilizing other Forge commands. - If you use environment variables to store your credentials, the Forge CLI will use them regardless of whether there are credentials stored in a local keychain.
Next steps
You're all set up to build a Forge app in Bitbucket, Confluence, Jira, or Jira Service Management.
Rate this page: