Core concepts
Forge Feature Flags is now available as part of Forge Early Access Program (EAP). To start testing this feature, sign up using this form.
Forge Feature Flags is an experimental feature offered to selected users for testing and feedback purposes. This feature is unsupported and subject to change without notice. Do not use Forge Feature Flags in apps that handle sensitive information and customer data. The Feature flags EAP is fully functional in development, staging, and production environments.
Note: Feature flags are not available in Atlassian Government Cloud or FedRAMP environments. See, Limitations.
This page explains the fundamental concepts behind feature flags and how they work in the Forge platform.
What are feature flags?
Feature flags (also known as feature toggles or feature switches) are a software development technique that allows you to enable or disable features in your application without deploying new code. They provide a way to control feature rollouts, conduct experiments, and manage deployments safely.
Key benefits:
- Safe deployments - Deploy code without immediately activating features
- Instant rollbacks - Disable problematic features instantly
- Gradual rollouts - Release features to specific user groups or percentages
- Customer-specific features - Enable premium features for specific customers
- Environment control - Test features in different environments
How do they work?
Feature flags work by separating feature deployment from feature activation:
- Code deployment - Your feature code is deployed to production but remains inactive
- Flag configuration - Feature flags are configured in the Atlassian Developer Console
- Runtime evaluation - When your app runs, it checks the flag configuration
- Feature activation - Features are enabled/disabled based on flag rules and conditions
Ways to use feature flags
Boolean flags
Simple on/off switches for features. Perfect for major feature rollouts.
1 2// Example usage if (featureFlags.checkFlag(user, 'new-dashboard-layout', false)) { // Show new dashboard } else { // Show old dashboard }
Use cases:
- Enable/disable entire features
- Major feature rollouts
- Emergency feature toggles
Percentage rollouts
Gradual feature releases to specific percentages of users.
1 2// Initialize the feature flags SDK const featureFlags = new ForgeFeatureFlags(); await featureFlags.initialize({ environment: "development" }); // target based on installation context i.e. 25% of sites const user = { identifiers: { installContext: context?.installContext, } }; const enabled = featureFlags.checkFlag(user, 'beta-feature', false); if (enabled) { // Show beta feature to 25% of sites }
Use cases:
- Testing features with limited exposure
- Gradual user adoption
- Risk mitigation
Note: During EAP, percentage updates must be adjusted manually.
User-based targeting
Enable features for specific users or organizations.
1 2// Initialize the feature flags SDK const featureFlags = new ForgeFeatureFlags(); await featureFlags.initialize({ environment: "staging" }); const user = { identifiers:{ accountId: context?.principal?.accountId, }, attributes: { license: licenseValue, // "ACTIVE", "INACTIVE", "TRIAL" } }; // Example: Premium user targeting const result = featureFlags.checkFlag(user, 'premium-analytics');
Use cases:
- Premium features for enterprise customers
- Beta testing with specific users
- Customer-specific customizations
Environment-based flags
Different behavior across development, staging, and production environments.
1 2// Example: Debug mode in development // Initialize the feature flags SDK const featureFlags = new ForgeFeatureFlags(); await featureFlags.initialize({ environment: "development" }); if (featureFlags.checkFlag(user, 'debug-mode')) { console.log('Debug information'); }
Use cases:
- Development and testing features
- Environment-specific configurations
- Debug and logging controls
ID types: Understanding targeting contexts
One of the most important concepts developers need to understand when working with feature flags is ID type. The ID type determines the scope and context for flag evaluation, affecting how flags are targeted and evaluated.
installContext ID type
The installContext ID type targets feature flags at the app installation level. This means the flag evaluation is tied to where your Forge app is installed, not to individual users.
Key characteristics:
- Scope: App installation (e.g., a specific Jira or Confluence site)
- Persistence: Consistent across all users within that installation
- Use case: Site-wide features, organization-level configurations
When to use installContext:
- Enabling features for an entire organization/site
- Site-specific customizations or configurations
- Features that affect all users in a workspace
- Beta testing with specific customers/organizations
1 2// Initialize the feature flags SDK const featureFlags = new ForgeFeatureFlags(); await featureFlags.initialize({ environment: "development" }); const user = { identifiers:{ installContext: context?.installContext, }, attributes: { license: licenseValue, // "ACTIVE", "INACTIVE", "TRIAL" } }; // Example: Enable premium dashboard for specific installations const result = featureFlags.checkFlag(user, 'premium-dashboard-v2'); // This evaluates based on the installation context // All users in this installation will see the same result
Real-world example: Your app is installed on three different Jira sites:
- Acme Corp: Premium customer → Enable advanced reporting
- Beta Corp: Beta testing → Enable experimental features
- Demo Corp: Trial customer → Standard features only
accountID ID type
The accountID ID type targets feature flags at the individual user level using Atlassian account IDs. This enables precise user-based targeting and personalization.
Key characteristics:
- Scope: Individual Atlassian user account
- Persistence: Follows the user across installations (if they have access)
- Use case: User-specific features, personalized experiences
When to use accountID:
- Personalized user experiences
- User-specific feature rollouts
- Beta testing with individual users
- Premium features for specific user types
1 2// Initialize the feature flags SDK const featureFlags = new ForgeFeatureFlags(); await featureFlags.initialize({ environment: "development" }); const user = { identifiers:{ accountId: context?.principal?.accountId, }, attributes: { license: licenseValue, // "ACTIVE", "INACTIVE", "TRIAL" } }; // Example: Enable beta features for specific users const result = featureFlags.checkFlag(user, 'beta-user-interface'); // This evaluates based on the specific user
Real-world example: Within the same installation, different users see different features:
- Admin users: Full feature set enabled
- Beta users: Early access to new features
- Regular users: Standard feature set
Choosing the right ID type
| Scenario | ID Type | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Enable premium features for enterprise customers | installContext | Organization-level decision |
| Rollout new UI to 10% of users | accountID | User-level randomization |
| Beta test with specific organizations | installContext | Site-wide testing |
| Personalized dashboard layouts | accountID | User-specific preferences |
| Site-specific integrations | installContext | Installation-level configuration |
| A/B testing user flows | accountID | Individual user tracking |
Technical considerations
installContext evaluation:
1 2// Initialize the feature flags SDK const featureFlags = new ForgeFeatureFlags(); await featureFlags.initialize({ environment: "development" }); const user = { identifiers:{ installContext: context?.installContext, } }; const result = featureFlags.checkFlag(user, 'org-wide-feature');
accountID evaluation:
1 2// Initialize the feature flags SDK const featureFlags = new ForgeFeatureFlags(); await featureFlags.initialize({ environment: "development" }); const user = { identifiers:{ accountId: context?.principal?.accountId, } }; const result = featureFlags.checkFlag(user, 'user-specific-feature');
Best practices:
- Start with installContext for broader organizational features
- Use accountID when you need user-level control
- Document your ID type choice in flag descriptions
- Consider privacy implications when using accountID targeting
- Plan for mixed scenarios where some flags use installContext and others use accountID
Attributes
Developers can target feature flags based on app context using predefined attributes. The following attributes are supported:
| Attribute name | Type | Description | Example value(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| installContext | string | The ARI identifying the cloud or Atlassian app context of this component installation. | ari:cloud:ecosystem::app/1234-abcd-5678-efgh |
| accountId | string | The principal containing the Atlassian ID of the user that interacted with the component. | 5b10ac8d82e05b22cc7d4ef5 |
| appVersion | string | The version of the app. | 1.2.3 |
| license | string | Contains information about the license of the app. This field is only present for paid apps in the production environment. license is undefined for free apps, apps in DEVELOPMENT and STAGING environments, and apps that are not listed on the Atlassian Marketplace. | ACTIVE, INACTIVE, TRIAL |
| capabilitySet | string | The capability level of the app license. | capabilityAdvanced, capabilityStandard |
Basic example using predefined values:
1 2// Initialize the feature flags SDK const featureFlags = new ForgeFeatureFlags(); await featureFlags.initialize({ environment: "development" }); const user = { identifiers: { installContext: "ari:cloud:ecosystem::app/1234-abcd-5678-efgh", accountId: "5b10ac8d82e05b22cc7d4ef5" }, attributes: { appVersion: "1.2.3", license: "ACTIVE", capabilitySet: "capabilityAdvanced" } }; const isEnabled = featureFlags.checkFlag(user, "new-feature");
Custom attributes
If the predefined attributes don't meet your needs, you can use custom attributes for targeting.
Here's a quick demonstration of how to create custom attributes in the Developer Console:
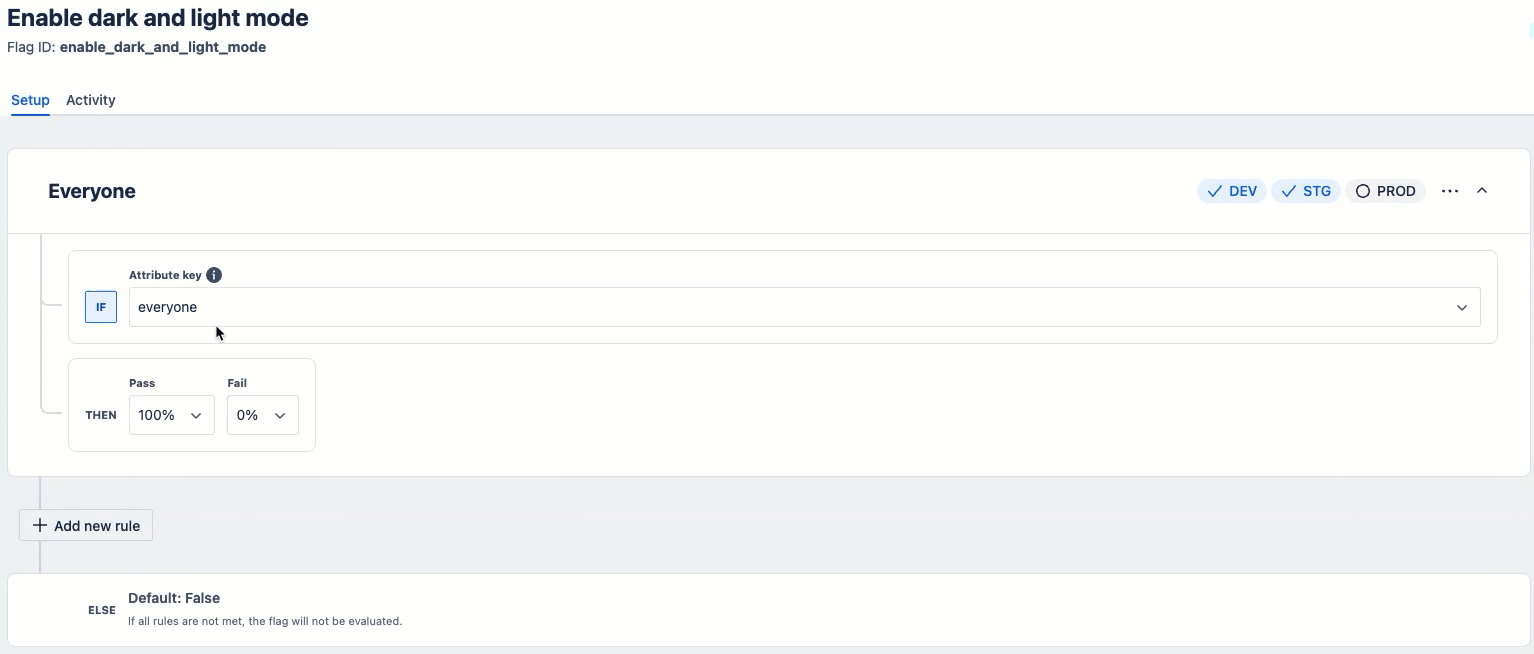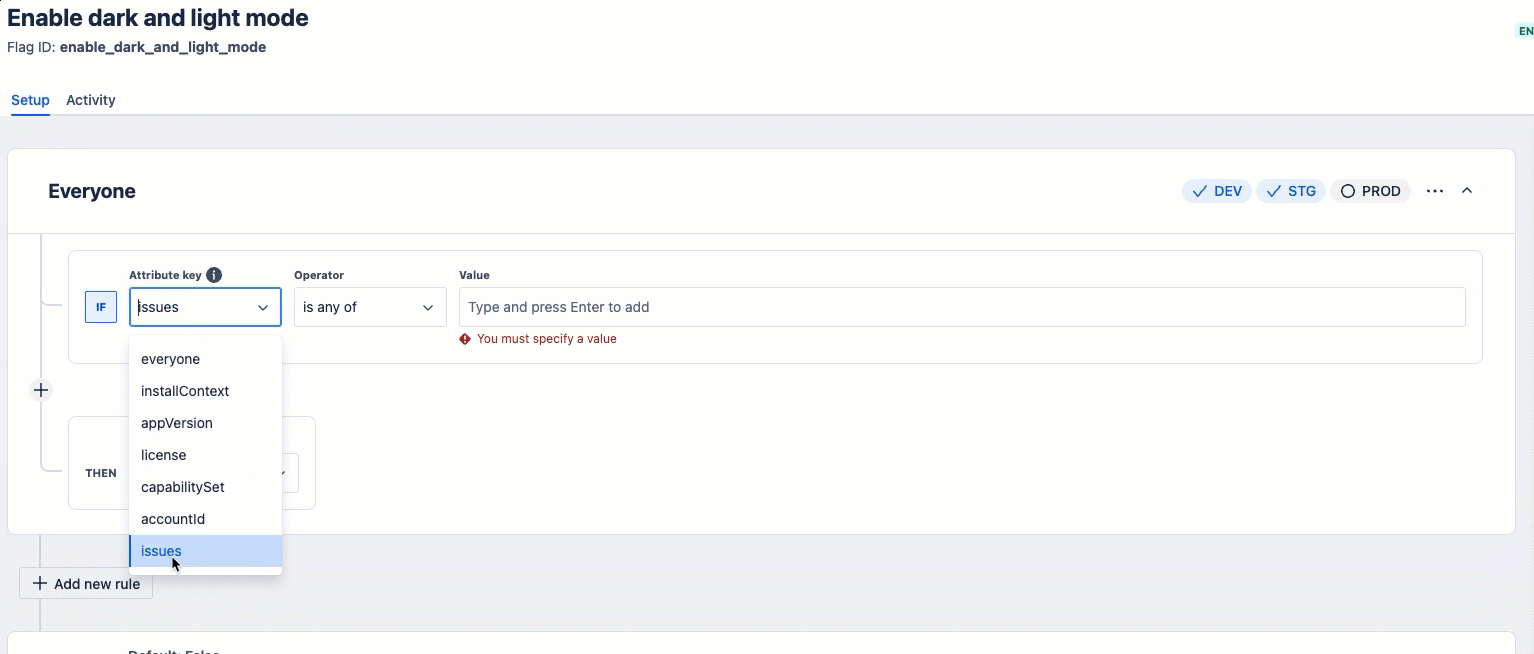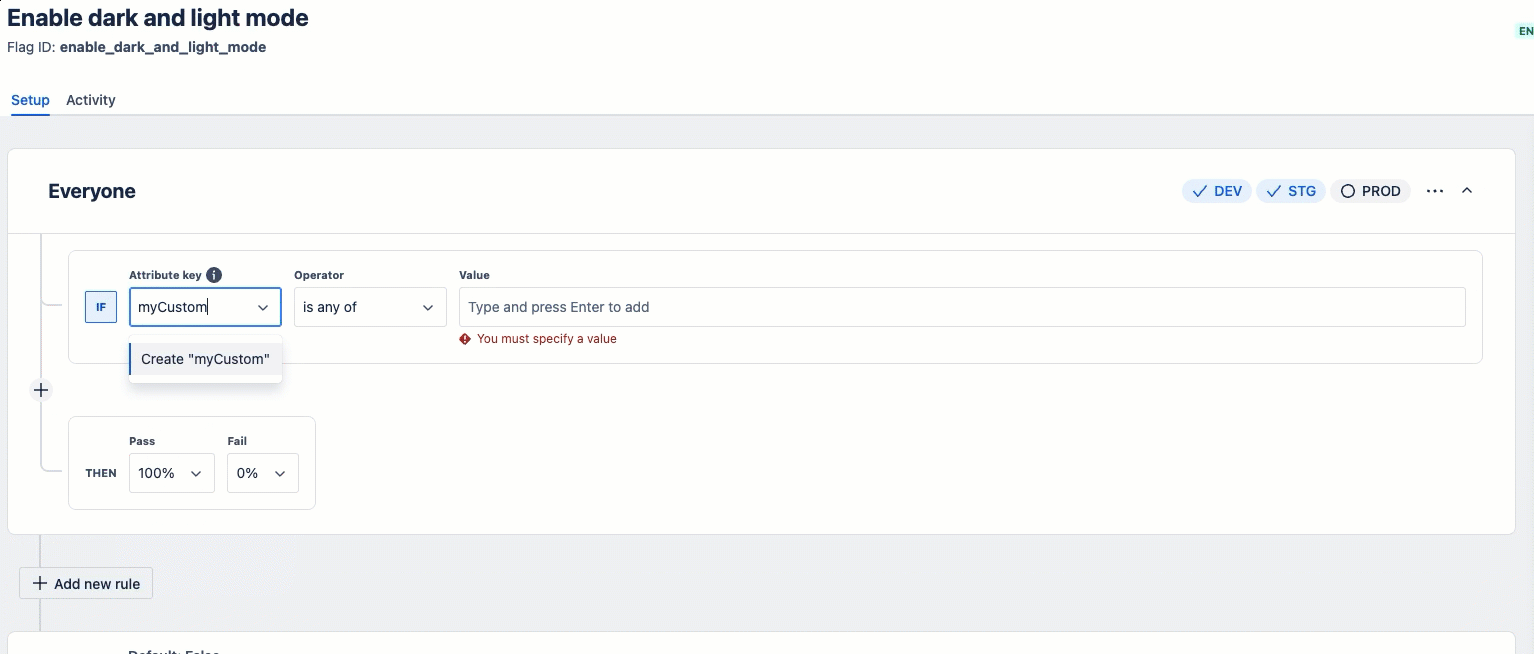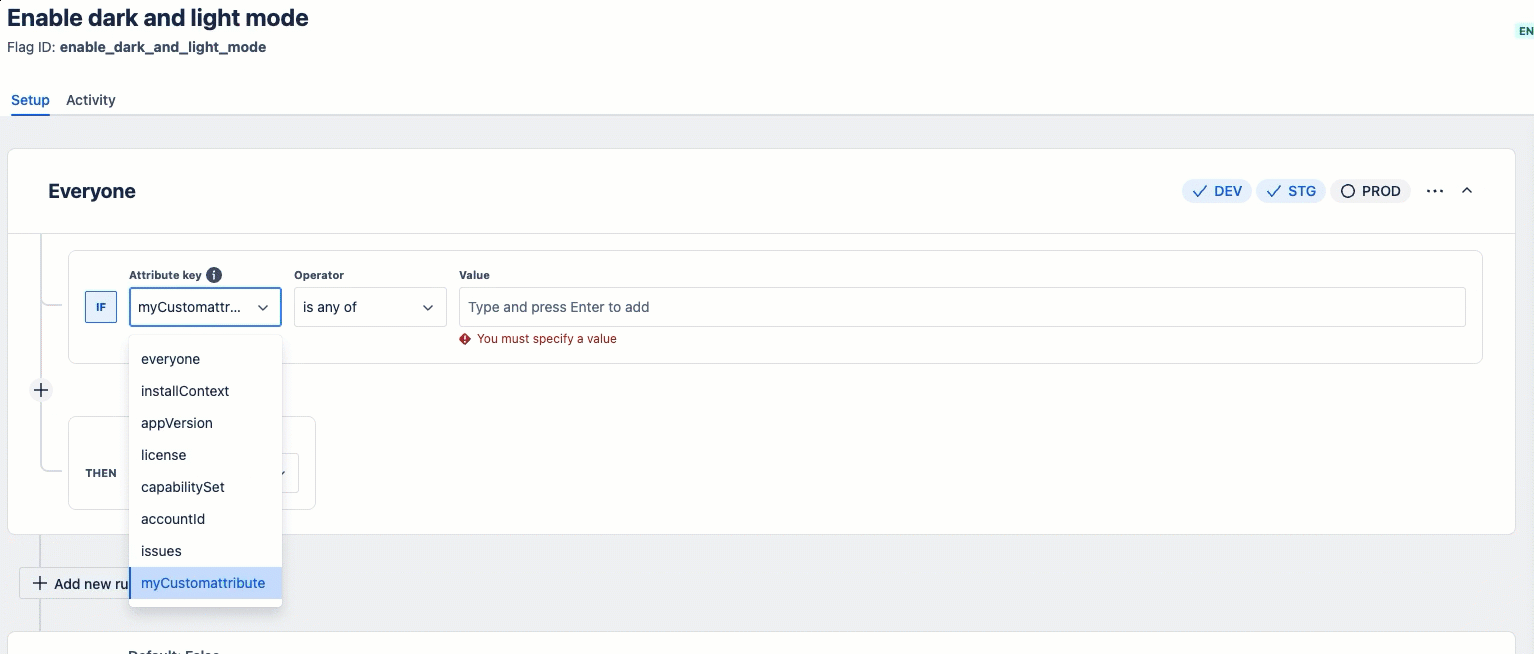
Basic example showing custom attributes:
1 2// Initialize the feature flags SDK const featureFlags = new ForgeFeatureFlags(); await featureFlags.initialize({ environment: environmentType?.toLowerCase() || "development" }); const user = { identifiers: { installContext: context?.installContext, }, attributes: { issues: 4 // Number of issues in a Jira board } }; const isEnabled = featureFlags.checkFlag(user, "new-feature");
Feature flag lifecycle
Creation → Configuration → Evaluation → Cleanup
1. Creation
Define the flag in Developer Console with:
- Name - Human-readable description
- Flag ID - Unique identifier used in code
- Description - Purpose and expected behavior
- ID Type - Target scope (InstallContext, User, etc.)
2. Configuration
Set up rules, targeting, and rollout percentages:
- Rules - Conditions for when the flag is enabled
- Targeting - Specific users, organizations, or percentages
- Environments - Which environments the flag applies to
3. Evaluation
App checks flag status at runtime:
- API call -
featureFlags.checkFlag(user, flagId) - Rule evaluation - System applies configured rules
- Result - Boolean or object with flag state
4. Monitoring
Track flag usage and performance:
- Limited monitoring - Basic flag management only (analytics not available during EAP)
- Performance considerations - Be aware of potential latency impact
- Manual tracking - Use application logs for diagnostics
5. Cleanup
Remove flags when no longer needed:
- Migration - Ensure all users are on new behavior
- Deletion - Remove from Developer Console
Best practices
Naming conventions
- Include team/component context:
team-dashboard-redesign
Monitoring and maintenance
- Be aware of potential performance impact (feature flags SDK initialization latency)
- Regularly review and clean up unused flags
- Use application logs to track flag usage manually (no built-in analytics during EAP)
- Plan for manual percentage rollout adjustments
Current EAP limitations
During the Early Access Program, the following features are not available:
- Analytics - No built-in evaluation metrics or success rates
- Scheduled rollouts - No automated time-based progression
- A/B/C testing - No built-in experimentation framework
- Cross-app management - No centralized flag management
- Manual percentage updates - Must manually adjust percentage rollouts
- Performance considerations - Feature flags SDK initialization may add latency to app startup
For complete details, see Limitations.
Next steps
Rate this page: